- 2.1. Introduction
- 2.2. The n queens example
- 2.3. The Manners 2009 example
- 2.4. The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) example
- 2.5. The Traveling Tournament Problem (TTP) example
- 2.6. Cloud balancing
- 2.7. The ITC 2007 curriculum course example
- 2.8. The ITC 2007 examination example
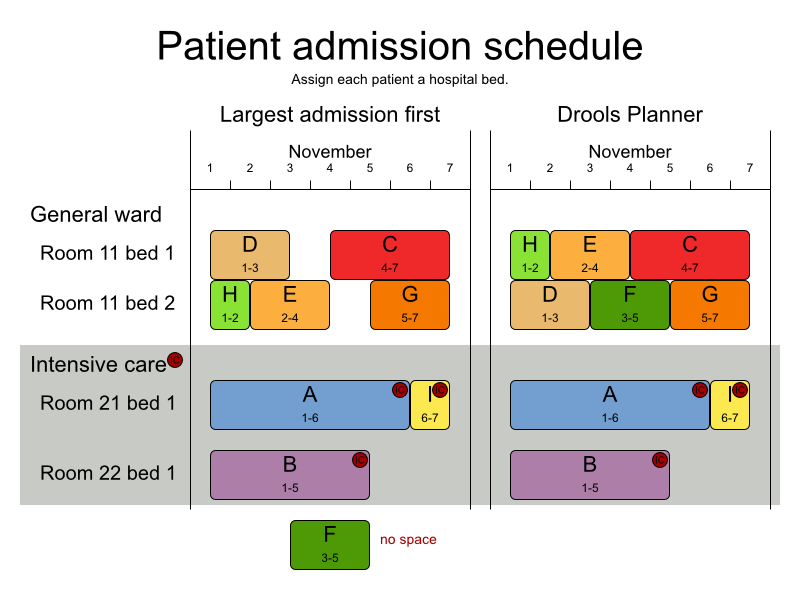
- 2.9. The patient admission scheduling (PAS) example (hospital bed planning)
- 2.10. The INRC 2010 nurse rostering example
Drools Planner has several examples. In this manual we explain Drools Planner mainly using the n queens example. So it's advisable to read at least the section about that example. For advanced users, the following examples are recommended: curriculum course, examination and nurse rostering.
You can find the source code of all these examples in the drools source distribution and also in git under
drools-planner/drools-planner-examples.
The n queens puzzle is a puzzle with the follow constraints:
Use a chessboard of n rows and n columns.
Place n queens on the chessboard.
No 2 queens can attack each other. Note that a queen can attack any other queen on the same horizontal, vertical or diagonal line.
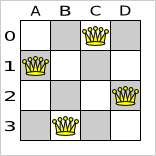
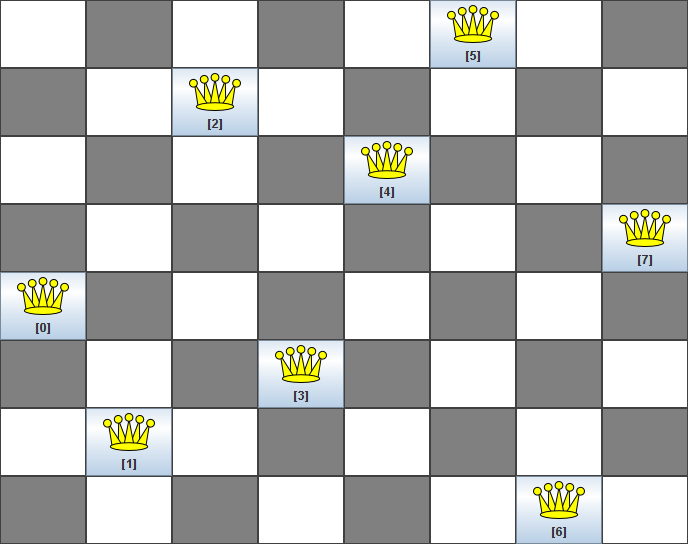
The most common n queens puzzle is the 8 queens puzzle, with n = 8. We 'll explain Drools Planner using the 4 queens puzzle as the primary example.
A proposed solution could be:
The above solution is wrong because queens A1 and B0 can attack each other (as can queens B0 and D0). Removing queen B0 would respect the "no 2 queens can attack each other" constraint, but would break the "place n queens" constraint.
Below is a correct solution:
All the constraints have been met, so the solution is correct. Note that most n queens puzzles have multiple correct solutions. We 'll focus on finding a single correct solution for a given n, not on finding the number of possible correct solutions for a given n.
These numbers might give you some insight on the size of this problem.
Table 2.1. NQueens problem size
| # queens (n) | # possible solutions (each queen its own column) | # feasible solutions (distinct) | # optimal solutions (distinct) | # possible / # optimal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 256 | 2 | 2 | 128 |
| 8 | 16777216 | 64 | 64 | 262144 |
| 16 | 18446744073709551616 | 14772512 | 14772512 | 1248720872503 |
| 32 | 1.46150163733090291820368483e+48 | ? | ? | ? |
| 64 | 3.94020061963944792122790401e+115 | ? | ? | ? |
| n | n ^ n | ? | # feasible solutions | ? |
The Drools Planner implementation has not been optimized because it functions as a beginner example. Nevertheless, it can easily handle 64 queens.
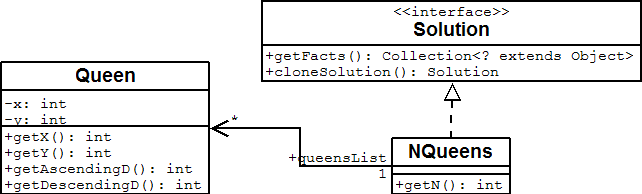
Use a good domain model and it will be easier to understand and solve your problem with Drools Planner. We 'll use this domain model for the n queens example:
A Queen instance has an x (its column, for example: 0 is column A, 1 is column B, ...)
and a y (its row, for example: 0 is row 0, 1 is row 1, ...). Based on the x and y, the ascending diagonal line as
well as the descending diagonal line can be calculated. The x and y indexes start from the upper left corner of
the chessboard.
Table 2.2. A solution for the 4 queens puzzle shown in the domain model
| A solution | Queen | x | y | ascendingD (x + y) | descendingD (x - y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
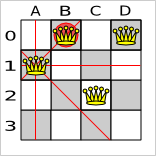 | A1 | 0 | 1 | 1 (**) | -1 |
| B0 | 1 | 0 (*) | 1 (**) | 1 | |
| C2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | |
| D0 | 3 | 0 (*) | 3 | 3 |
A single NQueens instance contains a list of all Queen instances. It
is the Solution implementation which will be supplied to and retrieved from the Solver. Notice
that in the 4 queens example, NQueens's getN() method will always return 4.
In Manners 2009, miss Manners is throwing a party again.
This time she invited 144 guests and prepared 12 round tables with 12 seats each.
Every guest should sit next to someone (left and right) of the opposite gender.
And that neighbour should have at least one hobby in common with the guest.
Also, this time there should be 2 politicians, 2 doctors, 2 socialites, 2 sports stars, 2 teachers and 2 programmers at each table.
And the 2 politicians, 2 doctors, 2 sports stars and 2 programmers shouldn't be the same kind.
Drools Expert also has the normal miss Manners examples (which is much smaller) and employs a brute force heurstic to solve it. Drools Planner's implementation employs far more scalable heuristics while still using Drools Expert to calculate the score..
Given a list of cities, find the shortest tour for a salesman that visits each city exactly once. See the wikipedia definition of the traveling Salesman Problem.
It is one of the most intensively studied problems in computational mathematics. Yet, in the real world, it's often only part of a planning problem, along with other constraints, such as employee shift time constraints.
Schedule matches between N teams with the following hard constraints:
Each team plays twice against every other team: once home and once away.
Each team has exactly 1 match on each timeslot.
No team must have more than 3 consecutive home or 3 consecutive away matches.
No repeaters: no 2 consecutive matches of the same 2 opposing teams.
and the following soft constraint:
Minimize the total distance traveled by all teams.
The problem is defined on this webpage (which contains several world records too).
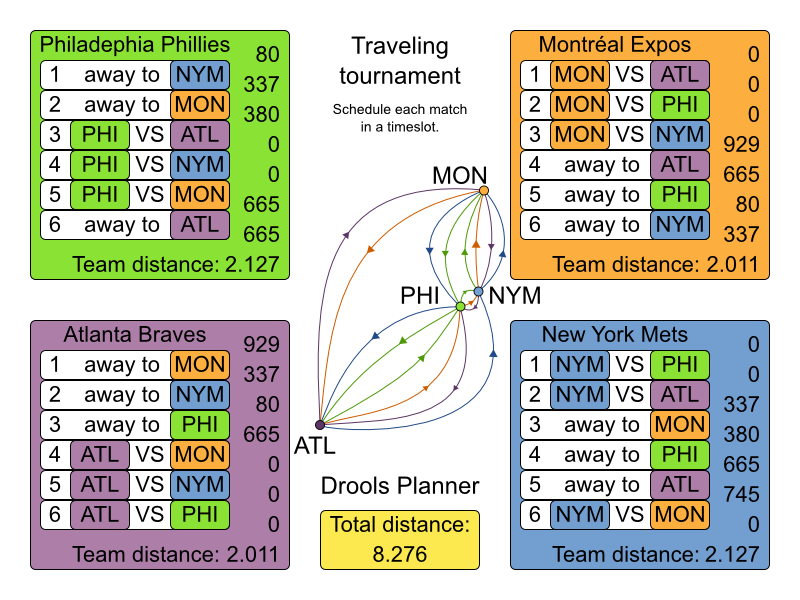
There are 2 implementations (simple and smart) to demonstrate the importance of some performance tips. The
DroolsPlannerExamplesApp always runs the smart implementation, but with these commands you can
compare the 2 implementations yourself:
$ mvn exec:exec -Dexec.mainClass="org.drools.planner.examples.travelingtournament.app.simple.SimpleTravelingTournamentApp" ... $ mvn exec:exec -Dexec.mainClass="org.drools.planner.examples.travelingtournament.app.smart.SmartTravelingTournamentApp" ...
The smart implementation performs and scales exponentially better than the simple implementation.
These numbers might give you some insight on the size of this problem.
Table 2.3. Traveling tournament problem size
| # teams | # days | # matches | # possible solutions (simple) | # possible solutions (smart) | # feasible solutions | # optimal solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 6 | 12 | 2176782336 | <= 518400 | ? | 1? |
| 6 | 10 | 30 | 1000000000000000000000000000000 | <= 47784725839872000000 | ? | 1? |
| 8 | 14 | 56 | 1.52464943788290465606136043e+64 | <= 5.77608277425558771434498864e+43 | ? | 1? |
| 10 | 18 | 90 | 9.43029892325559280477052413e+112 | <= 1.07573451027871200629339068e+79 | ? | 1? |
| 12 | 22 | 132 | 1.58414112478195320415135060e+177 | <= 2.01650616733413376416949843e+126 | ? | 1? |
| 14 | 26 | 182 | 3.35080635695103223315189511e+257 | <= 1.73513467024013808570420241e+186 | ? | 1? |
| 16 | 30 | 240 | 3.22924601799855400751522483e+354 | <= 2.45064610271441678267620602e+259 | ? | 1? |
| n | 2 * (n - 1) | n * (n - 1) | (2 * (n - 1)) ^ (n * (n - 1)) | <= (((2 * (n - 1))!) ^ (n / 2)) | ? | 1? |
There are a number of computers available. Assign a list of processes on those computers.
Hard constraints:
Every computer should be able to handle the sum of each of the minimal hardware requirements (CPR, RAM, network bandwith) of all its processes.
Soft constraints:
Each computer that has one or more processes assigned, has a fixed cost. Minimize the total cost.
This is a form of bin packing.
Schedule lectures into rooms and time periods.
The problem is defined by the International Timetabling Competition 2007 track 3.
Schedule each exam into a period and into a room. Multiple exams can share the same room during the same period.
There are a number of hard constraints that cannot be broken:
Exam conflict: 2 exams that share students should not occur in the same period.
Room capacity: A room's seating capacity should suffice at all times.
Period duration: A period's duration should suffice for all of its exams.
Period related hard constraints should be fulfilled:
Coincidence: 2 exams should use the same period (but possibly another room).
Exclusion: 2 exams should not use the same period.
After: 1 exam should occur in a period after another exam's period.
Room related hard constraints should be fulfilled:
Exclusive: 1 exam should not have to share its room with any other exam.
There are also a number of soft constraints that should be minimized (each of which has parameterized penalty's):
2 exams in a row.
2 exams in a day.
Period spread: 2 exams that share students should be a number of periods apart.
Mixed durations: 2 exams that share a room should not have different durations.
Front load: Large exams should be scheduled earlier in the schedule.
Period penalty: Some periods have a penalty when used.
Room penalty: Some rooms have a penalty when used.
It uses large test data sets of real-life universities.
The problem is defined by the International Timetabling Competition 2007 track 1.
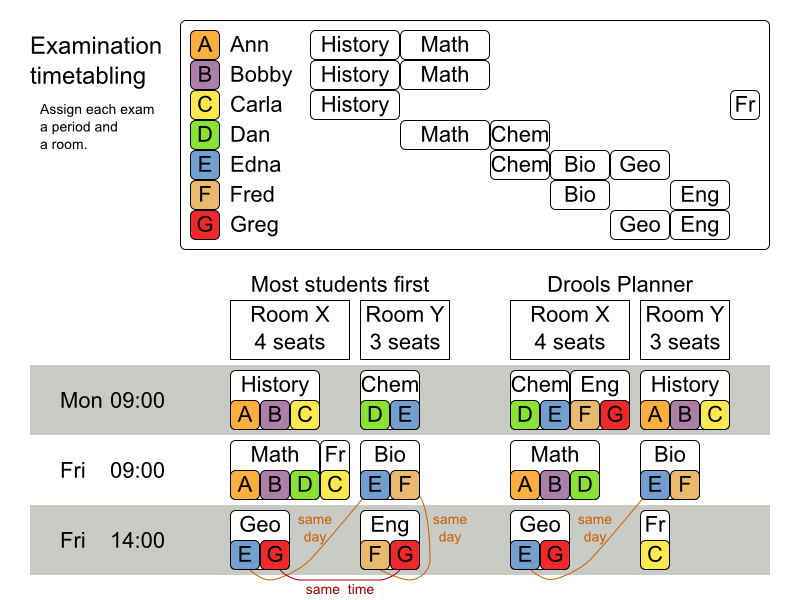
These numbers might give you some insight on the size of this problem.
Table 2.4. Examination problem size
| Set | # students | # exams/topics | # periods | # rooms | # possible solutions | # feasible solutions | # optimal solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| exam_comp_set1 | 7883 | 607 | 54 | 7 | 10^1564 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set2 | 12484 | 870 | 40 | 49 | 10^2864 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set3 | 16365 | 934 | 36 | 48 | 10^3023 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set4 | 4421 | 273 | 21 | 1 | 10^360 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set5 | 8719 | 1018 | 42 | 3 | 10^2138 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set6 | 7909 | 242 | 16 | 8 | 10^509 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set7 | 13795 | 1096 | 80 | 28 | 10^3671 | ? | 1? |
| exam_comp_set8 | 7718 | 598 | 80 | 8 | 10^1678 | ? | 1? |
| ? | s | t | p | r | (p * r) ^ e | ? | 1? |
Geoffrey De Smet (the Drools Planner lead) finished 4th in the International Timetabling Competition 2007's examination track with a very early version of Drools Planner. Many improvements have been made since then.
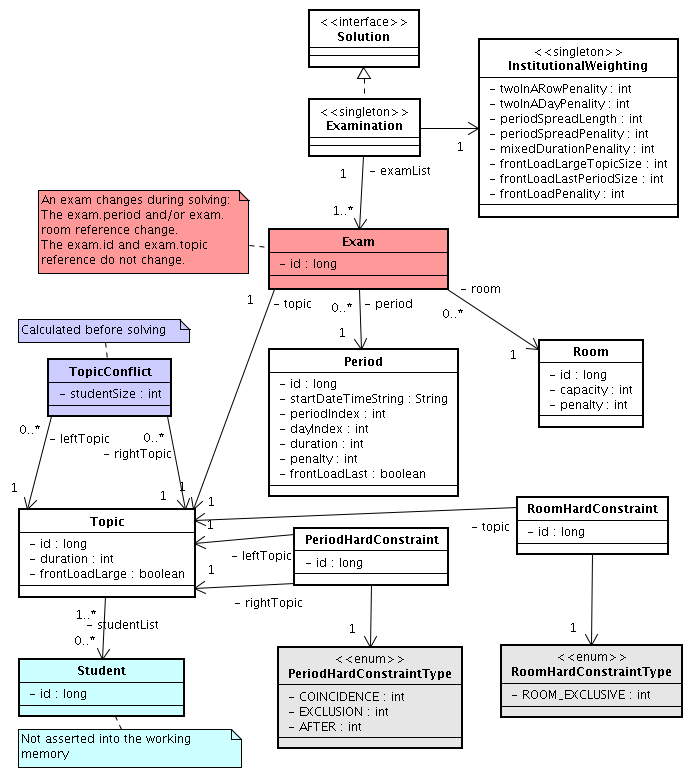
Below you can see the main examination domain classes:
Notice that we've split up the exam concept into an Exam class and a
Topic class. The Exam instances change during solving, when they get another
period or room property. The Topic, Period and Room
instances never change during solving.
In this problem, we have to assign each patient (that will come to the hospital) a bed for each night that the patient will stay in the hospital. Each bed belongs to a room and each room belongs to a department. The arrival and departure dates of the patients is fixed: only a bed needs to be assigned for each night.
There are a couple of hard constraints:
2 patients shouldn't be assigned to the same bed in the same night.
A room can have a gender limitation: only females, only males, the same gender in the same night or no gender limitation at all.
A department can have a minimum or maximum age.
A patient can require a room with specific equipment(s).
And of course, there are also some soft constraints:
A patient can prefer a maximum room size, for example if he/she want a single room.
A patient is best assigned to a department that specializes in his/her problem.
A patient is best assigned to a room that specializes in his/her problem.
A patient can prefer a room with specific equipment(s).
The problem is defined on this webpage and the test data comes from real world hospitals.
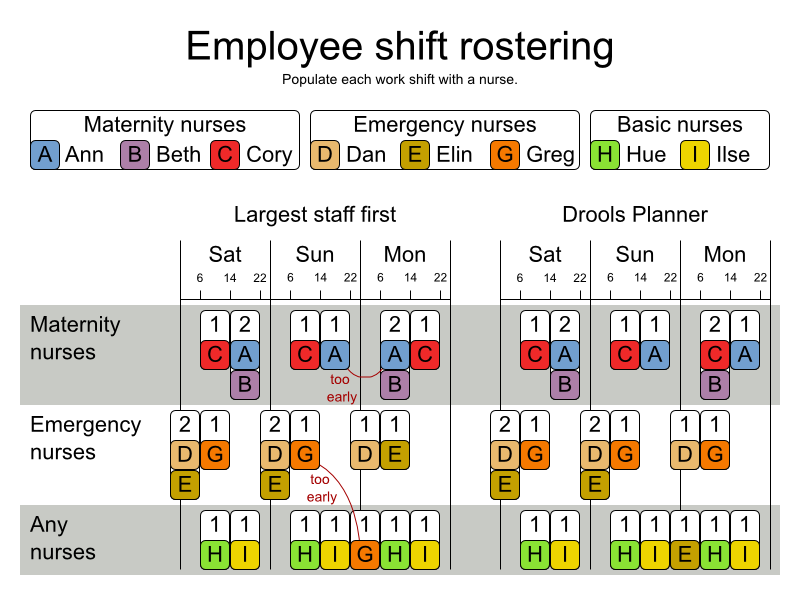
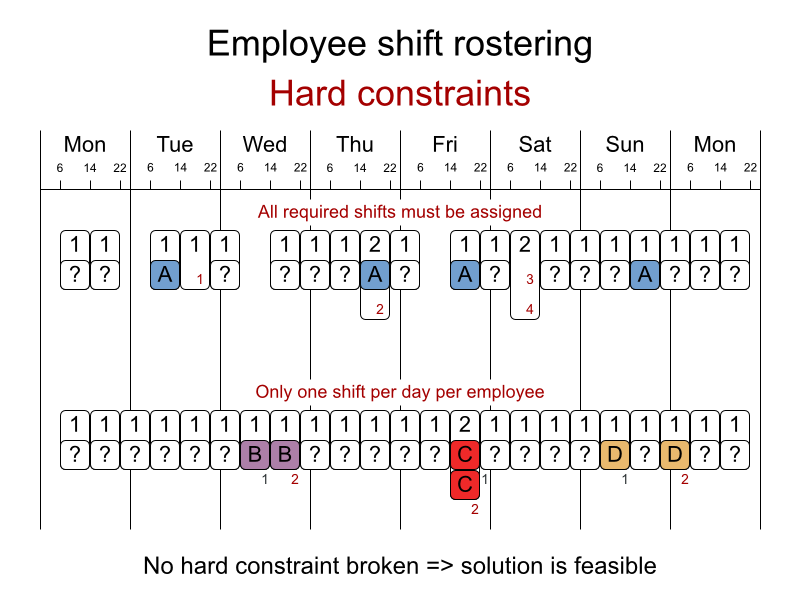
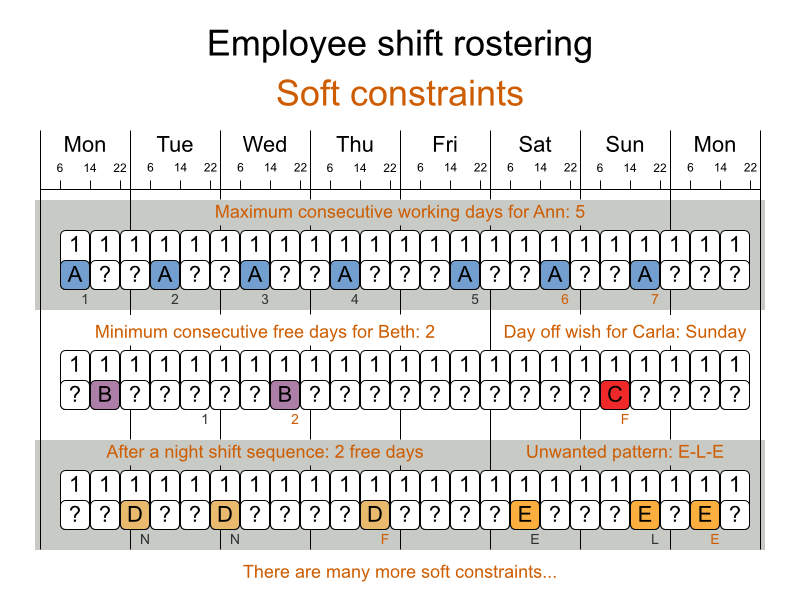
Schedule nurses into shifts.
The problem is defined by the International Nurse Rostering Competition 2010.