- 4.1. Version management
- 4.2. The Asset Editor
- 4.3. Creating a package
- 4.4. Spring Contexts
- 4.5. Working Sets
- 4.6. Business rules with the guided editor
- 4.7. DSL rules
- 4.8. Technical rules (DRL)
- 4.9. Spreadsheet decision tables
- 4.10. Guided decision tables (web based)
- 4.11. Templates of assets/rules
- 4.12. The Fact Model
- 4.13. Functions
- 4.14. DSL editor
- 4.15. Rule flows
- 4.16. BPMN2 Process
- 4.17. Work Item Definition
- 4.18. Data enumerations (drop down list configurations)
- 4.19. Test Scenario
- 4.20. File
- 4.21. Change-Set
- 4.22. Services
- 4.23. **INCUBATOR FEATURE** New Rule Asset - Scorecards
Both assets and whole packages of assets are "versioned" in the Guvnor, but the mechanism is slightly different. Individual assets are saved a bit like a version of a file in a source control system. However, packages of assets are versioned "on demand" by taking a snapshot (typically which is used for deployment). The next section talks about deployment management and snapshots.
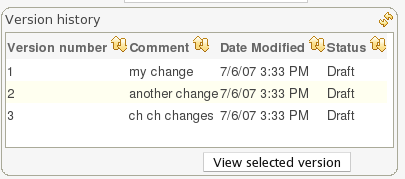
Each time you make a change to an asset, it creates a new item in the version history. This is a bit like having an unlimited undo. You can look back through the history of an individual asset like the list above, and view it (and restore it) from that point in time.
The Asset Editor is the principle component of Guvnor's User-Interface. It consists of two tabs:-
Attributes
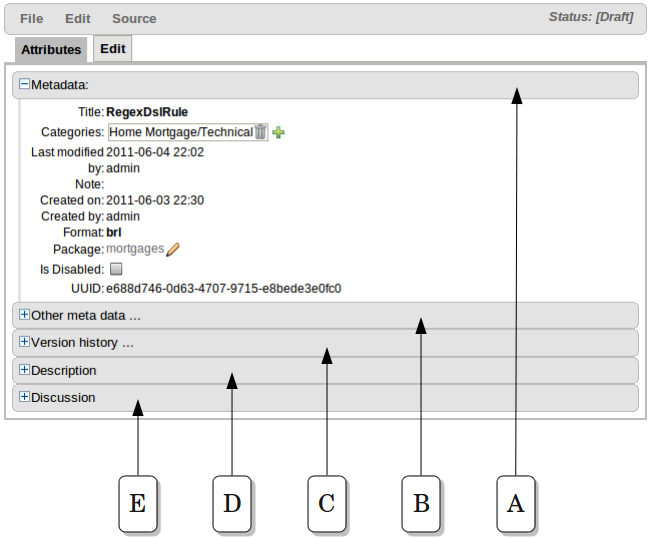
A : Meta data (from the "Dublin Core" standard):-
"Last modified:" The last modified date.
"By:" Who made the last change.
"Note:" A comment made when the Asset was last updated (i.e. why a change was made)
"Created on:" The date and time the Asset was created.
"Created by:" Who initially authored the Asset.
"Format:" The short format name of the type of Asset.
"Package:" The package to which the Asset belongs.
"Is Disabled:" Whether the Asset has been disabled from inclusion in a binary package.
"UUID:" A unique identifier for the Asset version.
B : Other miscellaneous meta data for the Asset.
C : Version history of the Asset.
D : Free-format documentation\description for the Asset. It is encouraged, but not mandatory, to record a description of the Asset before editing.
E : Discussions regarding development of the Asset can be recorded here.
Edit
A : The Asset editor is where the "editor widget" lives - exactly what form the editor takes depends on the Asset type.
B : These are menus contains various actions for the Asset; such as Saving, Archiving, changing Status etc.
C : The current status of the Asset.
Configuring packages is generally something that is done once, and by someone with some experience with rules/models. Generally speaking, very few people will need to configure packages, and once they are setup, they can be copied over and over if needed. Package configuration is most definitely a technical task that requires the appropriate expertise.
All assets live in "packages" in the Guvnor - a package is like a folder (it also serves as a "namespace"). A home folder for rule assets to live in. Rules in particular need to know what the fact model is, what the namespace is etc.
So while rules (and assets in general) can appear in any number of categories, they only live in one package. If you think of the Guvnor as a file system, then each package is a folder, and the assets live in that folder - as one big happy list of files. When you create a deployment snapshot of a package, you are effectively copying all the assets in that "folder" into another special "folder".
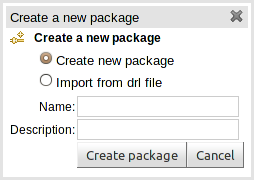
To create an empty package select "New Package" from the "Create new" (asset) menu.
An empty package can be created by simply specifying a name and optional description.
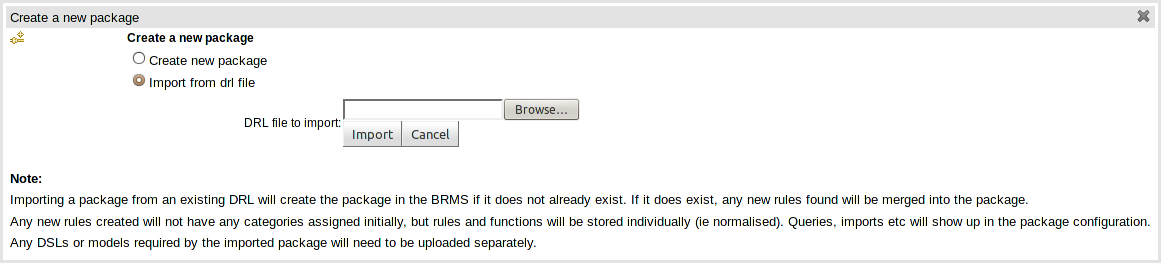
It is also possible to create a package by importing an existing DRL
file. When you choose to create a new package, you can choose an option to
upload a .drl file. The Guvnor will then attempt to
understand that DRL, break create a package for you. The rules in it will
be stored as individual assets (but still as DRL text content). Note that
to actually build the package, you will need to upload an appropriate
model (as a JAR) to validate against, as a separate step.
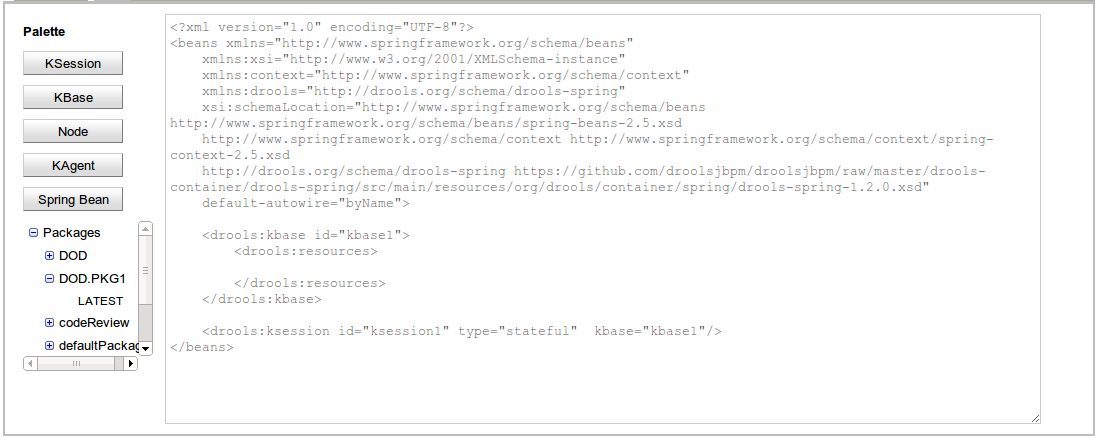
This textual editor allows you to define Drools (and potentially any) Spring context file. These files are later accessible through HTTP.
The editor comes with a basic pallete that you can use to paste predefined Spring Beans templates like kbases, ksessions and so on.
The pallete also has a Package tree that can be used to add resources to the Spring Context file being edited.
The Beans are inserted in the caret position of the editor
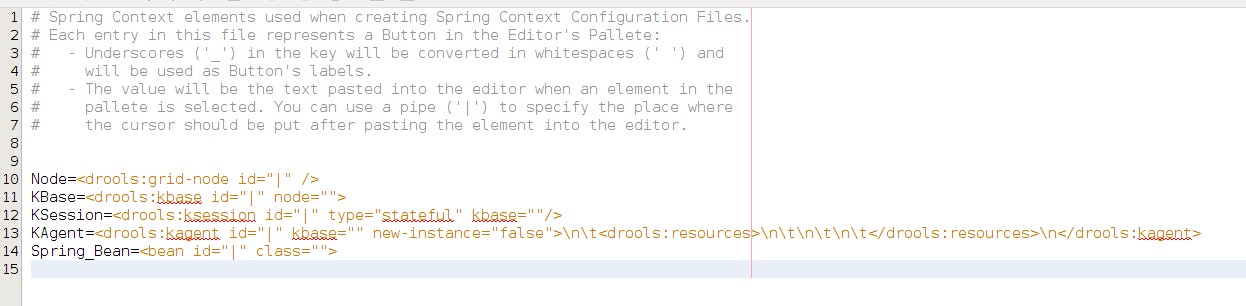
The elements in the pallete can be customized editing the file $GUVNOR_HOME/WEB-INF/Clases/springContextElements.properties
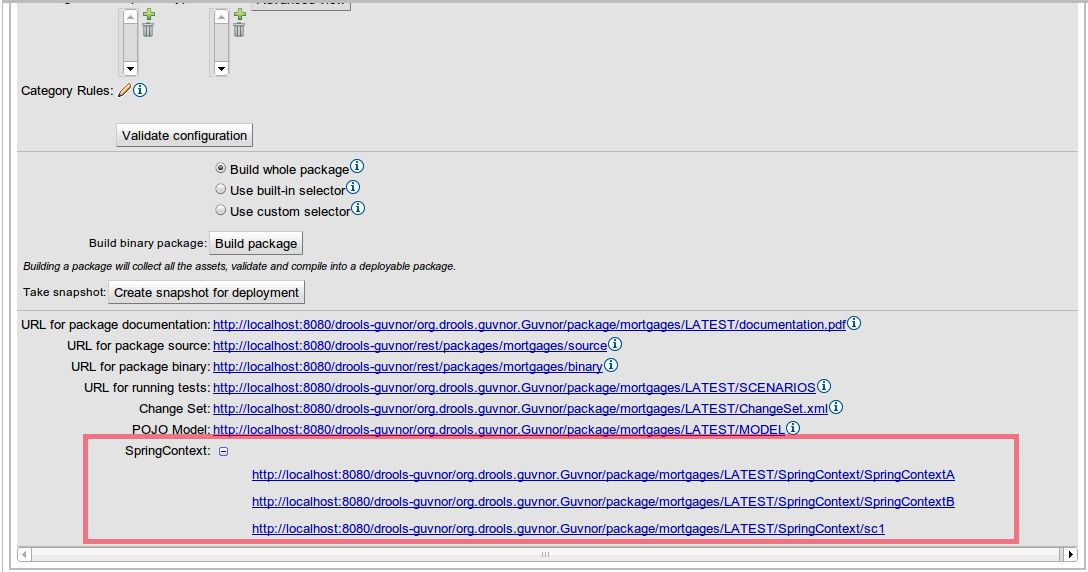
Each Spring Context has its own URL that applications can use to access it. These URLs are shown in the Package Edit Screen
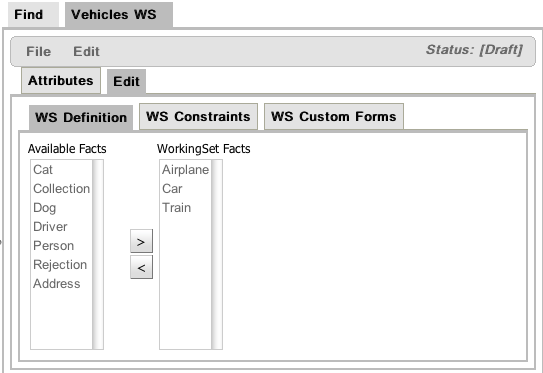
Working Sets are a mean for grouping Facts and then defining constraints on them. You can create groups of Facts and only those Facts will be visible when authoring rules using the Guided Editor.
Right now, Working Sets must be activated manually from the Guided Editor window (using the "Select Working Set" button placed in the toolbar). In the future, different Working Sets could be assigned to different users to reduce the scope and complexity when authoring rules.
The figure above shows the window used to create or modify Working Sets. In this window you will find 2 lists. The list on the left side contains the possible Fact Types that can be added to the Working Set. These facts are those defined/imported in the package's model. The list on the right side contains the allowed Fact Types of this Working Set. When this Working Sets is active, only those Fact Types could be used while authoring rules using the Guided BRL Editor
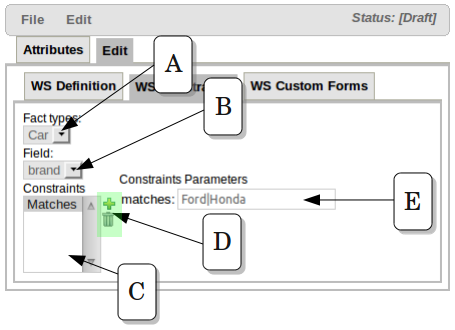
Once you have selected the valid Fact Types for a Working Set, you can add Constraints to the fields of those Facts Types. The image above shows how the Field Constraint tab looks like. In this configuration screen you will find:
A.- Fact Types dropdown: Here you will find a list containing the Working Set's Fact Types
B.- Field dropdown: Once you have selected a Fact Type, this dropdown will contain its fields.
C.- Constraints List: This lists shows all the Constraints applied to the selected Field
D.- Action Buttons: Using these buttons you will be able to add or remove Constraints to the selected Field. Right now, Guvnor provides a built-in collection of Constraints. The idea for next releases is to let users to plug their custom Constraints too.
E.- Constraint's Attributes: In this section you will find all the attributes of the current Constraint that could be parametrized by the user.
In the example above, a Matches Constraint is created for Car.brand field. This means that when rule authors use this field in a Rule condition, they should use a value valid according to this constraint, otherwise they will receive an error or warning.
Working Sets are no active by default in Guvnor. Because this is an experimental feature, you must enable them manually in the Guided Editor panel if you want to use them. In the future, Working Sets will be associated to each user's profile.
A new button was added in Guided Editor's Toolbar: "Select Working Sets". This button will open a popup with the list of the package's Working Sets. Using this popup you can activate one or more Working Sets.
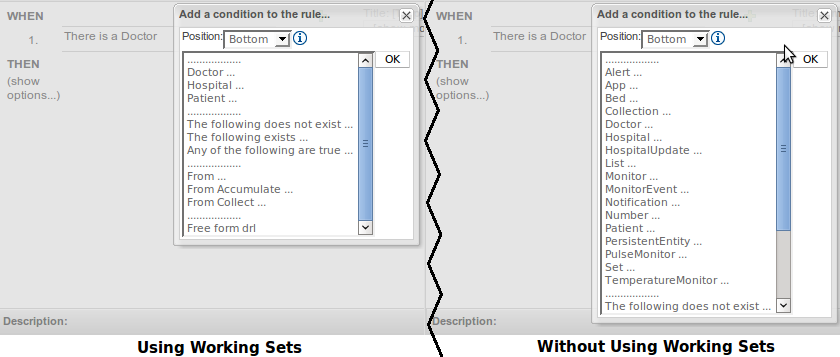
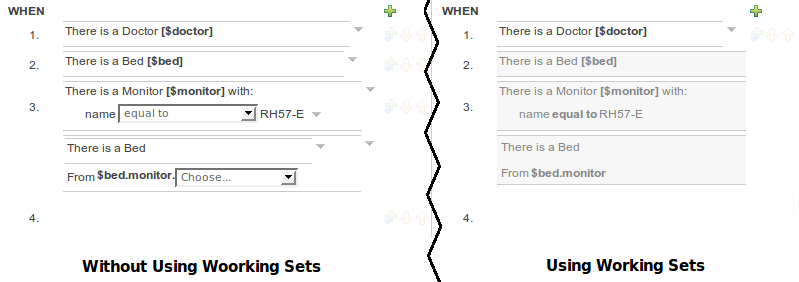
When Working Sets are activated, only the Fact Types allowed by them could be used when inserting new Patterns or Actions. The Patterns and Actions already present in the rule that contain prohibited Fact Types are marked as read only. Take a look at the next screen shots comparing the Guided Editor panel with and without Working Sets
In the image you can see how Working Sets could help rule's authors by reducing the amount of available Fact Types
Here you can see how Patterns containing prohibited Fact Types are switched to read only mode after Working Sets are activated.
Up to now we have only cover how Facts are filtered using Working Sets. Another important feature of Working Sets is Field Constraints. We have already saw how to configure them, now we are going to explain how to use them.
Because Field Constraints are defined inside a Working Set, we need to activate one or more Working Set to start working with them. Once a Working Set defining Field's Constraints is active we have two ways to use them: on demand validation and real-time validation.
On demand validation is performed when you press the "Verify" button present in Guided Editor's toolbar. This button will fire a rule verification and will end up showing a report with the results. Any violated constraint will be shown as an error or warning according to its relevance
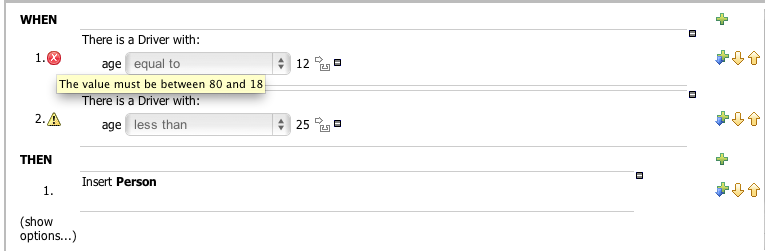
The image above shows the report that appears when a Working Set defines a Range Constraint on Driver.age. The age should be between 18 and 80.
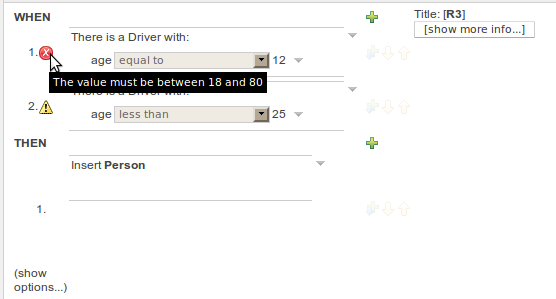
Real-Time validation is an experimental feature (yes, inside another experimental feature like Working Sets) that checks for Field's Constraints violations in real time and mark the lines where the violations are using error or warning icons. This feature is disabled by default because sometimes it could be expensive. If you want to try it out, you should enable it in Administration -> Rules Verification. This configuration is not yet persisted, so you need to enable it every time you start Guvnor.
This Image shows the result of real-time validation. There you can see the same result as on demand validation, but you don't need to click any button, and the errors/warnings are shown in a more fashionable way!
Warning
The problem with real-time validation is that right now only support "top level" Patterns.
Business Rules authored with the Guided Editor are more commonly known as "BRL Rules".
These rules use the guided GUI which controls and prompts user input based on knowledge of the object model.
This can also be augmented with DSL sentences.
Note
To use the Guided Rule Editor, someone will need to have you package configured before hand.
The Guided Rule Editor is composed of three main sections.
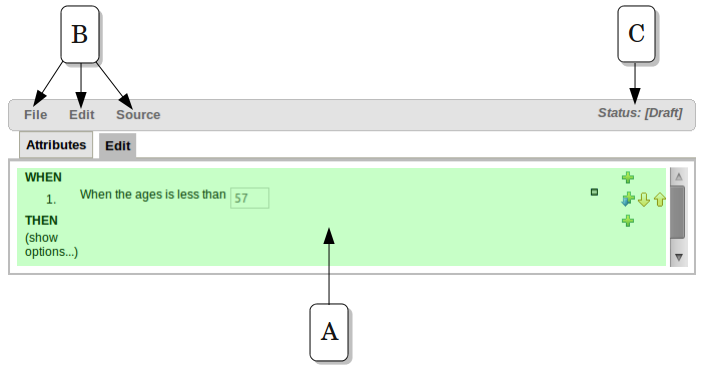
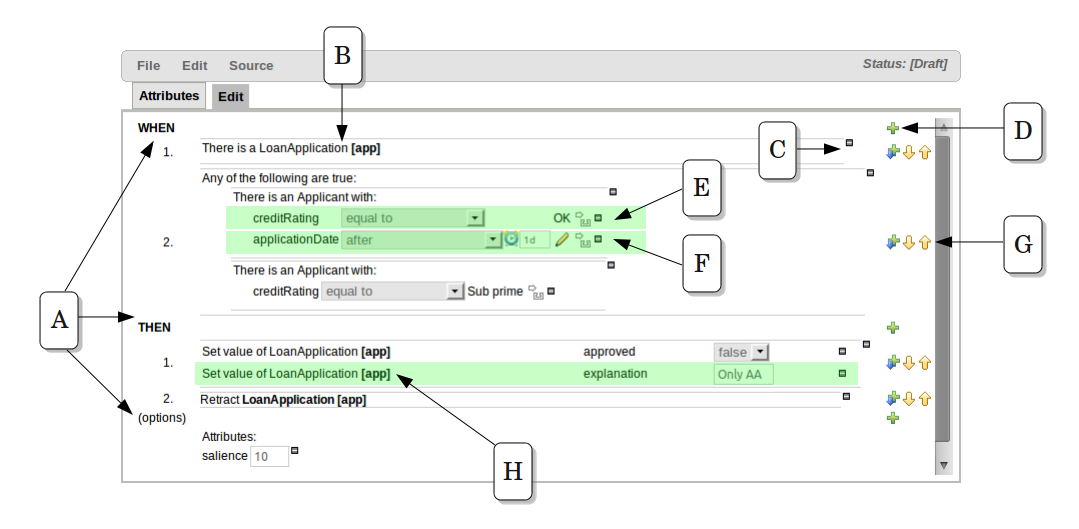
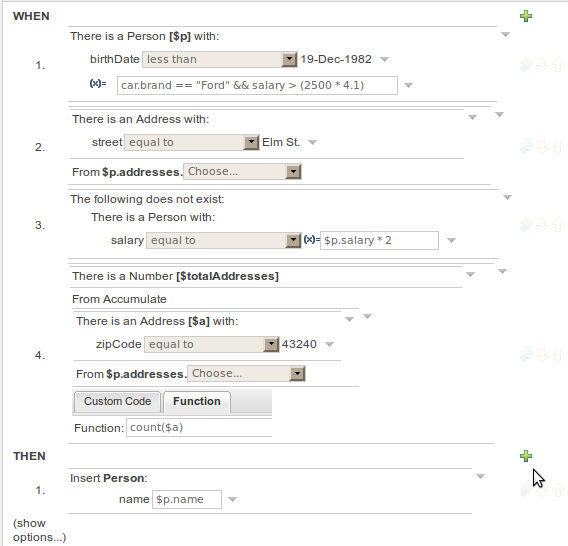
The following diagram shows the editor in action. The following descriptions apply to the lettered boxes in the diagram:-
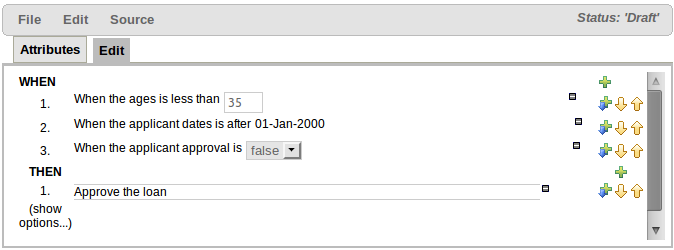
A : The different parts of a rule:-
The "WHEN" part, or conditions, of the rule.
The "THEN" action part of the rule.
Optional attributes that may effect the operation of the rule.
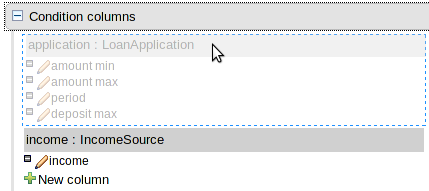
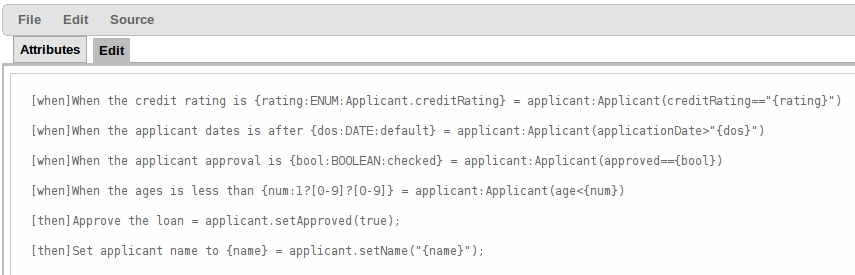
B : This shows a pattern which is declaring that the rule is looking for a "LoanApplication" fact (the fields are listed below, in this case none). Another pattern, "Applicant", is listed below "LoanApplication". Fields "creditRating" and "applicationDate" are listed. Clicking on the fact name ("LoanApplication") will pop-up a list of options to add to the fact declaration:-
Add more fields (e.g. their "location").
Assign a variable name to the fact (which you can use later on if needs be)
Add "multiple field" constraints - i.e. constraints that span across fields (e.g. age > 42 or risk > 2).
C : The "minus" icon ("[-]") indicates you can remove something. In this case it would remove the whole "LoanApplication" fact declaration. Depending upon the placement of the icon different components of the rule declaration can be removed, for example a Fact Pattern, Field Constraint, other Conditional Element ("exists", "not exists", "from" etc) or an Action.
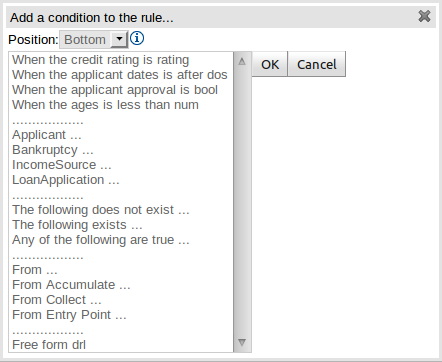
D : The "plus" icon ("+") allows you to add more patterns to the condition or the action part of the rule, or more attributes. In all cases, a popup option box is provided. For the "WHEN" part of the rule, you can choose from a list of Conditional Elements to add:
A Constraint on a Fact: it will give you a list of facts.
"The following does not exist": the fact plus constraints must not exist.
"The following exists": at least one match should exist (but there only needs to be one - it will not trigger for each match).
"Any of the following are true": any of the patterns can match (you then add patterns to these higher level patterns).
"From": this will insert a new From Conditional Element to the rule.
"From Accumulate": this will insert a new Accumulate Conditional Element to the rule.
"From Collect": this will insert a new Collect Conditional Element to the rule.
"From Entry-point": this allows you to define an Entry Point for the pattern.
"Free Form DRL": this will let you insert a free chunk of DRL.
If you just put a fact (like is shown above) then all the patterns are combined together so they are all true ("and").
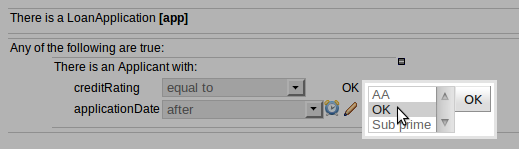
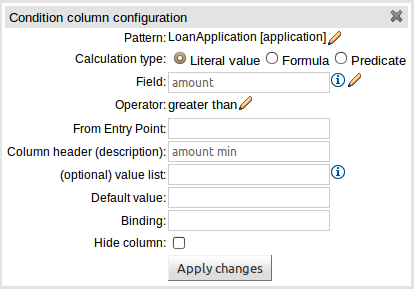
E : This shows the constraint for the "creditRating" field. Looking from left to right you find:-
The field name: "creditRating". Clicking on it you can assign a variable name to it, or access nested properties of it.
A list of constraint operations ("equal to" being selected): The content of this list changes depending on the field's data type.
The value field: It could be one of the following:-
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
String -> Textbox
Any numerical value -> Textbox restricting entry to values valid for the numerical sub-type (e.g. a byte can hold values from -128 to 127). BigDecimal and BigInteger data-types are also supported. Please ensure the appropriate Class has been imported in the Package configuration. The import will be added automatically if a POJO model has been uploaded that exposes an accessor or mutator for a BigDecimal or BigInteger field. BigDecimal values are automatically suffixed with "B" indicating to the underlying Engine that the literal value should be interpreted as a BigDecimal. BigIntegers are suffixed with "I". The user does not need to enter the suffix.
Date -> Calendar
Enumeration -> Listbox
Boolean -> Checkbox
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
An Expression - this will let you use an Expression Builder to build up a full mvel expression. (At the moment only basic expressions are supported)
F : This shows the constraint for the "applicationDate" field. Looking from left to right you find:
The field name: "applicationDate".
A list of constraint operations: "after" being selected.
A "clock" icon. Since the "applicationDate" is a Date data-type the list of available operators includes those relating to Complex Event Processing (CEP). When a CEP operator is used this additional icon is displayed to allow you to enter additional CEP operator parameters. Clicking the "clock" will cycle the available combinations of CEP operator parameters.
Note
Complex Event Processing operators are also available when the Fact has been declared as an event. Refer to the "Fact Model" chapter of this user-guide for details on how to add annotations to your Fact model. Events have access to the full range of CEP operators; Date field-types are restricted to "after", "before" and "coincides".
Note
Facts annotated as Events can also have CEP sliding windows defined.
When clicking on the + button of the WHEN section, a new popup will appear letting you to add a new Pattern to the Rule. The popup will looks similar to the image below. In this popup you could select the type of Pattern to add by selecting one of the list items. In the list you will have an entry for each defined Fact Type, in addition to the already mentioned Conditional Elements like "exists", "doesn't exist", "from", "collect", "accumulate", "from entry-point" and "free form DRL". Once you have selected one of this elements, you can add a new Pattern by clicking on the "Ok" button. The new pattern will be added at the bottom of the rule's left hand side. If you want to choose a different position, you can use the combobox placed at the top of the popup.
You can also open this popup by clicking in the [+] button from a Pattern's action toolbar. If that is the case, the pop-up that appears wouldn't constraint the position combobox, because the new Pattern will be added just after the Pattern where you clicked.
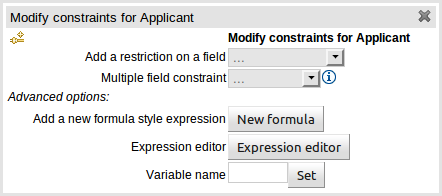
The below dialog is what you will get when you want to add constraints to a fact. In the top half are the simple options: you can either add a field constraint straight away (a list of fields of the applicable fact will be shown), or you can add a "Multiple field constraint" using AND or OR operands. In the bottom half of the window you have the Advanced options: you can add a formula (which resolves to True or False - this is like in the example above: "... salary > (2500 * 4.1)". You can also assign a Variable name to the fact (which means you can then access that variable on the action part of the rule, to set a value etc).
H : This shows an "action" of the rule, the Right Hand Side of a rule consists in a list of actions. In this case, we are updating the "explanation" field of the "LoanApplication" fact. There are quite a few other types of actions you can use:-
Insert a completely new Fact and optionally set a field on the Fact.
The value field can be one of the following:-
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
String -> Textbox
Any numerical value -> Textbox restricting entry to values valid for the numerical sub-type (e.g. a byte can hold values from -128 to 127). BigDecimal and BigInteger data-types are also supported. Please ensure the appropriate Class has been imported in the Package configuration. The import will be added automatically if a POJO model has been uploaded that exposes an accessor or mutator for a BigDecimal or BigInteger field. BigDecimal values are automatically suffixed with "B" indicating to the underlying Engine that the literal value should be interpreted as a BigDecimal. BigIntegers are suffixed with "I". The user does not need to enter the suffix.
Date -> Calendar
Enumeration -> Listbox
Boolean -> Checkbox
A variable bound to a Fact or Field in the left-hand side. The data-type of the field being set must match the data-type of the variable.
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
Logically insert a completely new Fact (see "Truth Maintenance" in the Expert documentation) and optionally set a field on the Fact.
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
The value field can be one of the following:-
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
String -> Textbox
Any numerical value -> Textbox restricting entry to values valid for the numerical sub-type (e.g. a byte can hold values from -128 to 127). BigDecimal and BigInteger data-types are also supported. Please ensure the appropriate Class has been imported in the Package configuration. The import will be added automatically if a POJO model has been uploaded that exposes an accessor or mutator for a BigDecimal or BigInteger field. BigDecimal values are automatically suffixed with "B" indicating to the underlying Engine that the literal value should be interpreted as a BigDecimal. BigIntegers are suffixed with "I". The user does not need to enter the suffix.
Date -> Calendar
Enumeration -> Listbox
Boolean -> Checkbox
A variable bound to a Fact or Field in the left-hand side. The data-type of the field being set must match the data-type of the variable.
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
A variable bound to a Fact or Field in the left-hand side. The data-type of the field being set must match the data-type of the variable.
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
Modify a field of an existing fact (which tells the engine the fact has changed).
The value field can be one of the following:-
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
String -> Textbox
Any numerical value -> Textbox restricting entry to values valid for the numerical sub-type (e.g. a byte can hold values from -128 to 127). BigDecimal and BigInteger data-types are also supported. Please ensure the appropriate Class has been imported in the Package configuration. The import will be added automatically if a POJO model has been uploaded that exposes an accessor or mutator for a BigDecimal or BigInteger field. BigDecimal values are automatically suffixed with "B" indicating to the underlying Engine that the literal value should be interpreted as a BigDecimal. BigIntegers are suffixed with "I". The user does not need to enter the suffix.
Date -> Calendar
Enumeration -> Listbox
Boolean -> Checkbox
A variable bound to a Fact or Field in the left-hand side. The data-type of the field being set must match the data-type of the variable.
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
Set a field on a fact (in which case the engine doesn't know about the change - normally because you are setting a result).
The value field can be one of the following:-
A literal value: depending on the field's data type different components will be displayed:
String -> Textbox
Any numerical value -> Textbox restricting entry to values valid for the numerical sub-type (e.g. a byte can hold values from -128 to 127). BigDecimal and BigInteger data-types are also supported. Please ensure the appropriate Class has been imported in the Package configuration. The import will be added automatically if a POJO model has been uploaded that exposes an accessor or mutator for a BigDecimal or BigInteger field. BigDecimal values are automatically suffixed with "B" indicating to the underlying Engine that the literal value should be interpreted as a BigDecimal. BigIntegers are suffixed with "I". The user does not need to enter the suffix.
Date -> Calendar
Enumeration -> Listbox
Boolean -> Checkbox
A variable bound to a Fact or Field in the left-hand side. The data-type of the field being set must match the data-type of the variable.
A "formula": this is an expression which is calculated (this is for advanced users only)
Retract a fact from the Engine's Working Memory.
Add Facts to existing global lists.
Call a method on a variable.
Write a chunk of free form code.
The attributes section of a rule provides the means to define metadata and attributes (such as "salience", "no-loop" etc).
Click on the "+" icon to add a new metadata or attribute definition. Each defined will appear listed in this section.
Click on the "-" icon beside each metadata or attribute to remove it.
G : Next to each Pattern or Action you will find a toolbar containing 3 buttons.
The first "+" icon lets you insert a new Pattern/Action at an arbitrary location. The other "+" icons allow you to insert a new Pattern/Action below that you have selected.
The remaining arrow icons allow you to move the current Pattern/Action up or down.
Note that is it possible to limit field values to items in a pre-configured list. This list is either defined by a Java enumeration or configured as part of the package (using a data enumeration to provide values for the drop down list). These values can be a fixed list, or (for example) loaded from a database. This is useful for codes, and other fields where there are set values. It is also possible to have what is displayed on screen, in a drop down, be different to the value (or code) used in a rule. See the section on data enumerations for how these are configured.
It is possible to define a list of values for one field that are dependent upon the value of one or more other fields, on the same Fact (e.g. a list of "Cities" depending on the selected "Country region"). Please refer to the section on "Enumerations" for more information.
If the package the rule is part of has a DSL configuration, when when you add conditions or actions, then it will provide a list of "DSL Sentences" which you can choose from - when you choose one, it will add a row to the rule - where the DSL specifies values come from a user, then a edit box (text) will be shown (so it ends up looking a bit like a form). This is optional, and there is another DSL editor. Please note that the DSL capabilities in this editor are slightly less then the full set of DSL features (basically you can do [when] and [then] sections of the DSL only - which is no different to drools 3 in effect).
The following diagram shows the DSL sentences in action in the guided editor:
In the above example, you can see how to use a mixture of Conditional Elements, literal values, and formulas. The rule has 4 "top level" Patterns and 1 Action. The "top level" Patterns are:
A Fact Pattern on Person. This Pattern contains two field constraints: one for birthDate field and the other one is a formula. Note that the value of the birthDate restriction is selected from a calendar. Another thing to note is that you can make calculations and use nested fields in the formula restriction (i.e. car.brand). Finally, we are setting a variable name ($p) to the Person Fact Type. You can then use this variable in other Patterns.
Note
The generated DRL from this Pattern will be:
$p : Person( birthDate < "19-Dec-1982" , eval( car.brand == "Ford" && salary > (2500 * 4.1) ))
A From Pattern. This condition will create a match for every Address whose street name is "Elm St." from the Person's list of addresses. The left side of the from is a regular Fact Pattern and the right side is an Expression Builder that let us inspect variable's fields.
Note
The generated DRL from this Pattern will be:
Address( street == "Elm St." ) from $p.addressesA "Not Exist" Conditional Element. This condition will match when its content doesn't create a match. In this case, its content is a regular Fact Pattern (on Person). In this Fact Pattern you can see how variables ($p) could be used inside a formula value.
Note
The generated DRL from this Pattern will be:
not Person( salary == ( $p.salary * 2 ) )A "From Accumulate" Conditional Element. This is maybe one of the most complex Patterns you can use. It consist in a Left Pattern (It must be a Fact Pattern. In this case is a Number Pattern. The Number is named $totalAddresses), a Source Pattern (Which could be a Fact Pattern, From, Collect or Accumulate conditional elements. In this case is an Address Pattern Restriction with a field restriction in its zip field) and a Formula Section where you can use any built-in or custom Accumulate Function (in this example a count() function is used). Basically, this Conditional Element will count the addresses having a zip code of 43240 from the Person's list of addresses.
Note
The generated DRL from this Pattern will be:
$totalAddresses : Number() from accumulate ($a : Address( zipCode == " 43240") from $p.addresses, count($a))
DSL rules are textual rules, that use a language configuration asset to control how they appear.
A dsl rule is a single rule. Referring to the picture above, you can a text editor. You can use the icons to the right to provide lists of conditions and actions to choose from (or else press Control + Space at the same time to pop up a list).
Technical (DRL) rules are stored as text - they can be managed in the Guvnor. A DRL can either be a whole chunk of rules, or an individual rule. if its an individual rule, no package statement or imports are required (in fact, you can skip the "rule" statement altogether, just use "when" and "then" to mark the condition and action sections respectively). Normally you would use the IDE to edit raw DRL files, since it has all the advanced tooling and content assistance and debugging. However, there are times when a rule may have to deal with something fairly technical in a package in Guvnor. In any typical package of rules, you generally have a need for some "technical rules" - you can mix and match all the rule types together of course.
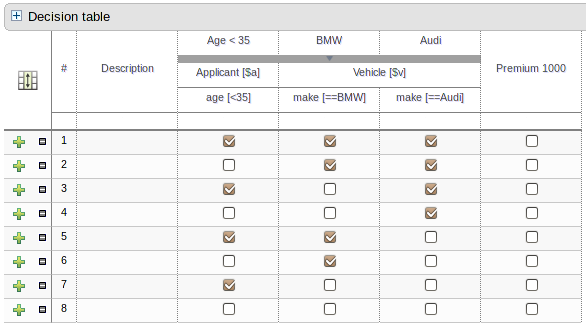
Multiple rules can be stored in a spreadsheet. Each row in the spreadsheet is a rule, and each column is either a condition, an action, or an option. The Drools Expert User Guide discusses spreadsheet decision tables in more detail.
To use a spreadsheet, you upload an XLS file (and can download the current version, as per the picture above). To create a new decision table, when you launch the rule wizard, you will get an option to create one (after that point, you can upload the XLS file).
The guided decision table feature allows decision tables to be edited in place on the web. This works similar to the guided editor by introspecting what facts and fields are available to guide the creation of a decision table. Rule attributes, meta-data, conditions and actions can be defined in a tabular format thus facilitating rapid entry of large sets of related rules. Web-based decision table rules are compiled into DRL like all other rule assets.
There are broadly two different types of decision table, both of which are supported in Guvnor:-
Extended Entry
Limited Entry
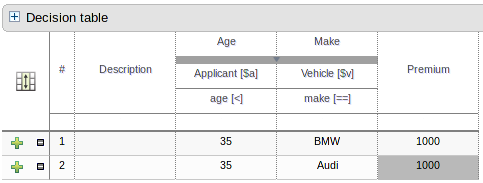
An Extended Entry decision table is one for which the column definitions, or stubs, specify Pattern, Field and operator but not value. The values, or states, are themselves held in the body of the decision table. It is normal, but not essential, for the range of possible values to be restricted by limiting entry to values from a list. Guvnor supports use of Java enumerations, Guvnor enumerations or decision table "optional value lists" to restrict value entry.
A Limited Entry decision table is one for which the column definitions specify value in addition to Pattern, Field and operator. The decision table states, held in the body of the table, are boolean where a positive value (a checked tick-box) has the effect of meaning the column should apply, or be matched. A negative value (a cleared tick-box) means the column does not apply.
The guided decision table is split into two main sections:-
The upper section allows table columns to be defined representing rule attributes, meta-data, conditions and actions.
The lower section contains the actual table itself; where individual rows define separate rules.
Cells can be selected in a variety of ways:-
Firstly individual cells can be double-clicked and a pop-up editor corresponding to the underlying data-type will appear. Groups of cells in the same column can be selected by either clicking in the first and dragging the mouse pointer or clicking in the first and clicking the extent of the required range with the shift key pressed.
Secondly the keyboard cursor keys can be used to navigate around the table. Pressing the enter key will pop-up the corresponding editor. Ranges can be selected by pressing the shift key whilst extending the range with the cursor keys.
Columns can be resized by hovering over the corresponding divider in the table header. The mouse cursor will change and then the column width dragged either narrower or wider.
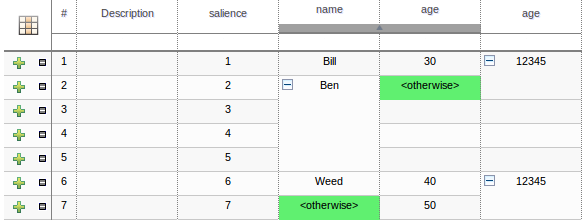
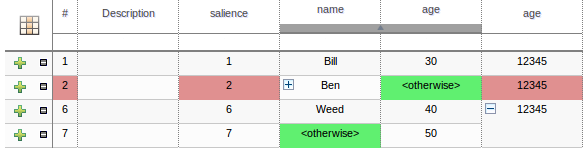
The icon in the top left of the decision table toggles cell merging on and off. When cells are merged those in the same column with identical values are merged into a single cell. This simplifies changing the value of multiple cells that shared the same original value. When cells are merged they also gain an icon in the top-left of the cell that allows rows spanning the merged cell to be grouped.
Cells that have been merged can be further collapsed into a single row. Clicking the [+\-] icon in the top left of a merged cell collapses the corresponding rows into a single entry. Cells in other columns spanning the collapsed rows that have identical values are shown unchanged. Cells in other columns spanning the collapsed rows that have different values are highlighted and the first value displayed.
When the value of a grouped cell is altered all cells that have been collapsed also have their values updated.
Condition columns defined with literal values that use either the equality (==) or inequality (!=) operators can take advantage of a special decision table cell value of "otherwise". This special value allows a rule to be defined that matches on all values not explicitly defined in all other rules defined in the table. This is best illustrated with an example:-
when
Cheese( name not in ("Cheddar", "Edam", "Brie") )
...
then
...
endwhen
Cheese( name in ("Cheddar", "Edam", "Brie") )
...
then
...
endWhole patterns and individual conditions can be re-arranged by dragging and dropping them in the configuration section of the screen. This allows constraints to be re-ordered to maximise performance of the resulting rules, by placing generalised constraints before more specific. Action columns can also be re-arranged by dragging and dropping them.
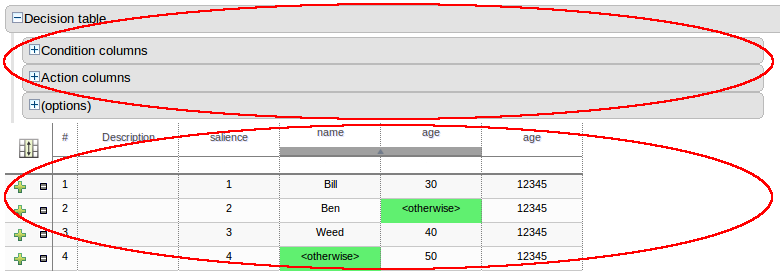
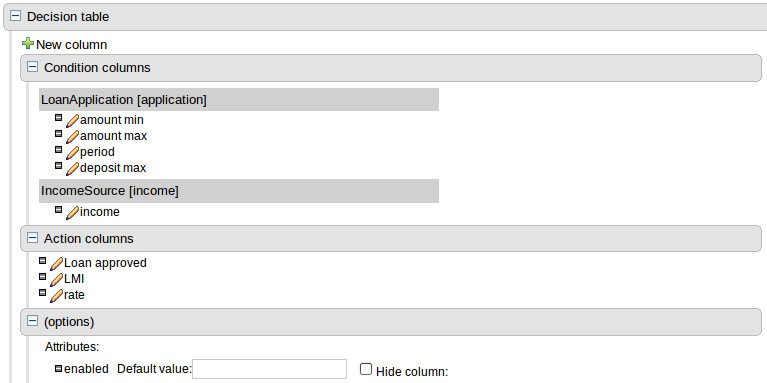
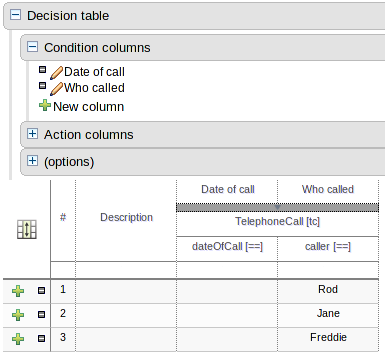
When a new empty decision table has been created you need to define columns for Facts, their constraints and corresponding actions.
Expand the "Decision table" element and you will see three further sections for "Conditions", "Actions" and "Options". Expanding either the "Conditions" or "Actions" sections reveals the "New column" icon. This can be used to add new column definitions to the corresponding section. Existing columns can be removed by clicking the "-" icon beside each column name, or edited by clicking the "pencil" icon also beside each column name. The "Options" section functions slightly differently however the principle is the same: clicking the "Add Attribute/Metadata" icon allows columns for table attributes to be defined (such as "salience", "no-loop" etc) or metadata added.
All decision table contain two utility columns containing rule number and rule description.
To add a column click on the "New column" icon.
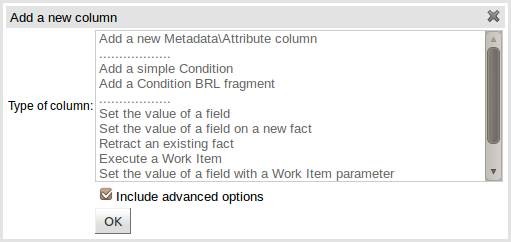
You are presented with the following column type selection popup.
By default the column type popup only shows the following simple types:-
Add a new Metadata\Attribute column
Add a simple Condition
Set the value of a field
Set the value of a field on a new fact
Retract an existing fact
Clicking on "Include advanced options" adds the following additional "advanced" column types for more advanced use cases:-
Add a Condition BRL fragment
Execute a Work Item
Set the value of a field with a Work Item parameter
Set the value of a field on a new Fact with a Work Item parameter
Add an Action BRL fragment
Zero or more meta-data columns can be defined, each represents the normal meta-data annotation on DRL rules.
Zero or more attribute columns representing any of the DRL rule attributes (e.g. salience, timer, enabled etc) can be added. An additional pseudo attribute is provide in the guided decision table editor to "negate" a rule. Use of this attribute allows complete rules to be negated. For example the following simple rule can be negated as also shown.
when $c : Cheese( name == "Cheddar" ) then ... end
when not Cheese( name == "Cheddar" ) then ... end
Conditions represent constraints on Fact Patterns defined in the left-hand side, or "when" portion, of a rule. To define a condition column you must first select or define a Fact Pattern bound to a model class. You can choose to negate the pattern. Once this has been completed you can define field constraints. If two or more columns are defined using the same fact pattern binding the field constraints become composite field constraints on the same pattern. If you define multiple bindings for a single model class each binding becomes a separate model class in the left-hand side of the rule.
When you edit or create a new column, you will be given a choice of the type of constraint:-
Literal : The value in the cell will be compared with the field using the operator.
Formula: The expression in the cell will be evaluated and then compared with the field.
Predicate : No field is needed, the expression will be evaluated to true or false.
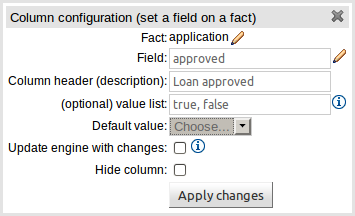
An Action to set the value of a field on previously bound fact. You have the option to notify the Rule Engine of the modified values which could lead to other rules being re-activated.
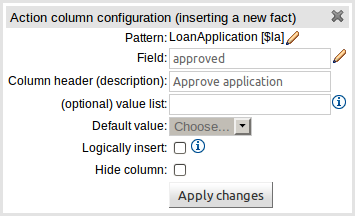
An Action to insert a new Fact into the Rule Engine Working Memory and set the a value of one of the new Facts' fields. You can choose to have the new Fact "logically inserted" meaning it will be automatically retracted should the conditions leading to the action being invoked cease to be true. Please refer to the Drools Expert documentation for details on Truth Maintenance and Logical insertions.
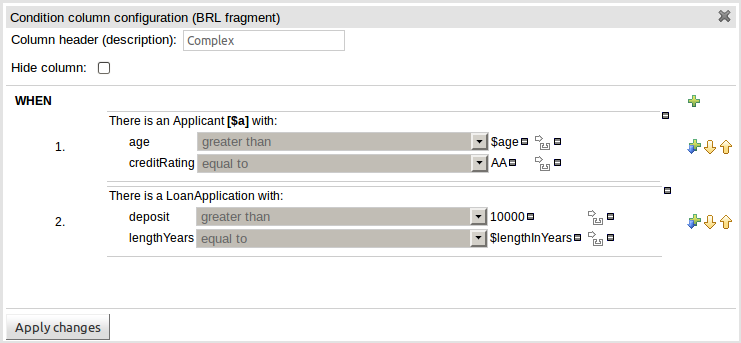
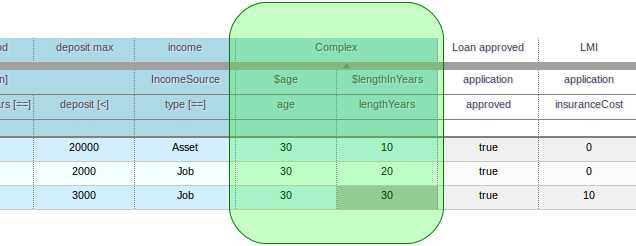
A construct that allows a BRL fragment to be used in the left-hand side of a rule. A BRL fragment is authored using the Guided Rule Editor and hence all features available in that editor can be used to define a decision table column; such as "from", "collect" and "accumulate" etc. When using the embedded Guided Rule Editor field values defined as "Template Keys" will form columns in the decision table. Facts and Fact's fields bound in the BRL fragment can be referenced by the simpler column types and vice-versa.
In the following example two Template Keys have been defined and hence two columns appear in the decision table.
An Action invoking a jBPM Work Item Handler setting it's input parameters to bound Facts\Facts fields values.
An Action setting the value of a Fact's field to that of a jBPM Work Item Handlers result parameter.
An Action setting the value of a new Fact's field to that of a jBOM Work Item Handlers result parameter.
A construct that allows a BRL fragment to be used in the right-hand side of a rule. A BRL fragment is authored using the Guided Rule Editor and hence all features available in that editor can be used to define a decision table column. When using the embedded Guided Rule Editor field values defined as "Template Keys" will form columns in the decision table. Facts bound in the BRL fragment can be referenced by the simpler column types and vice-versa.
In the following example two Template Keys have been defined and hence two columns appear in the decision table.
A Wizard can also be used to assist with defining the decision table columns.
The wizard can be chosen when first electing to create a new rule. The wizard provides a number of pages to define the table:-
Summary
Add Fact Patterns
Add Constraints
Add Actions to update facts
Add Actions to insert facts
Columns to expand
The "New Wizard" dialog shows a "Use wizard" checkbox when the asset type is set to "Decision Table (Web - guided editor)".
the summary page shows a few basic details about the decision table and allows the asset name to be changed.
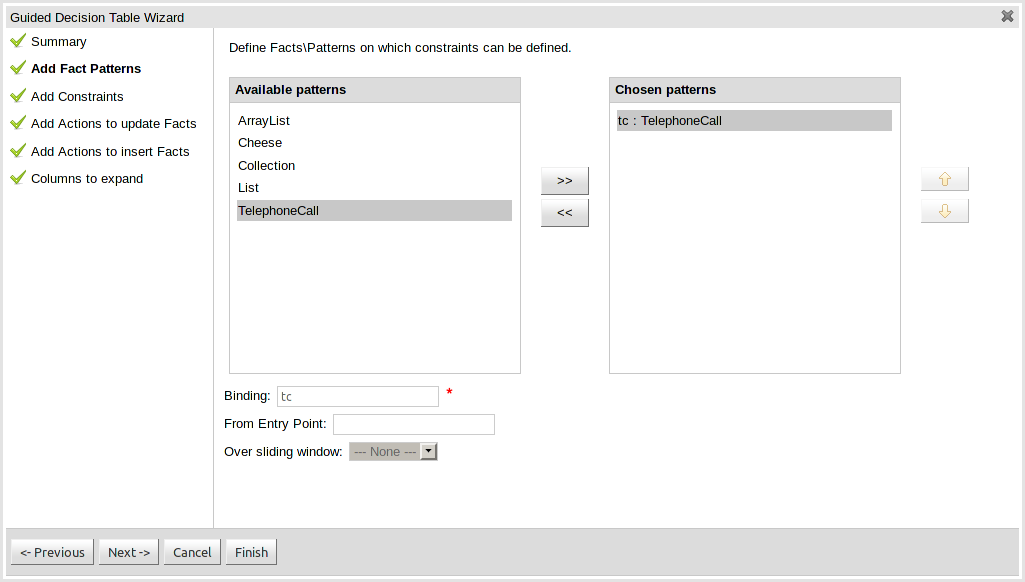
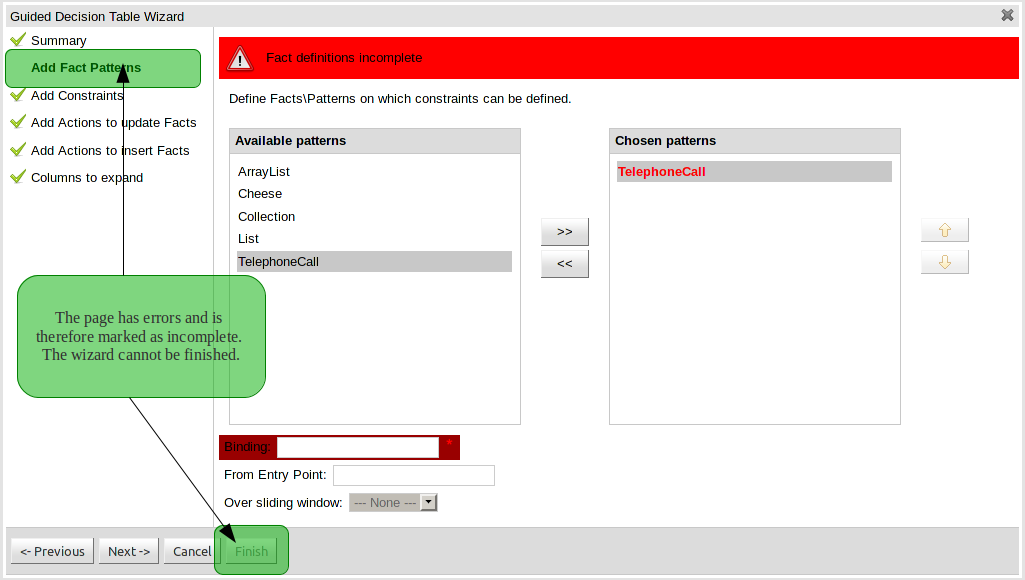
This page allows Fact types to be defined that will form the "When" columns of the rules. Fact types that are available in your model will be shown in the left-hand listbox. Select a Fact type and use the ">>" button to add it to your list of chosen facts on the right-hand listbox. Removal is a similar process: the Fact that is no longer required can be selected in the right-hand listbox and the "<<" button used to remove it. All Fact types need to be bound to a variable. Incomplete Fact types will be highlighted and a warning message displayed. You will be unable to finish your definition until all warnings have been resolved.
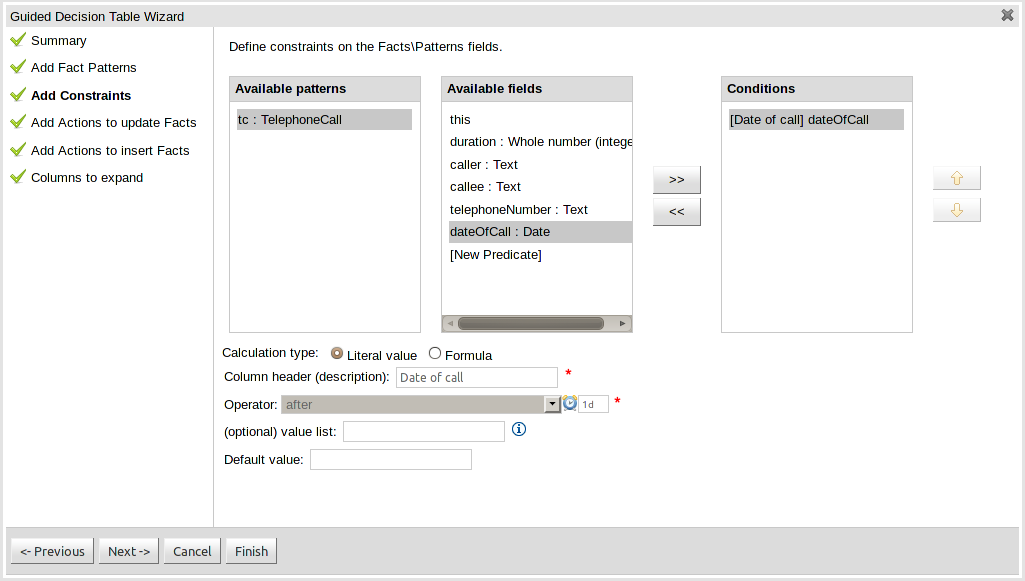
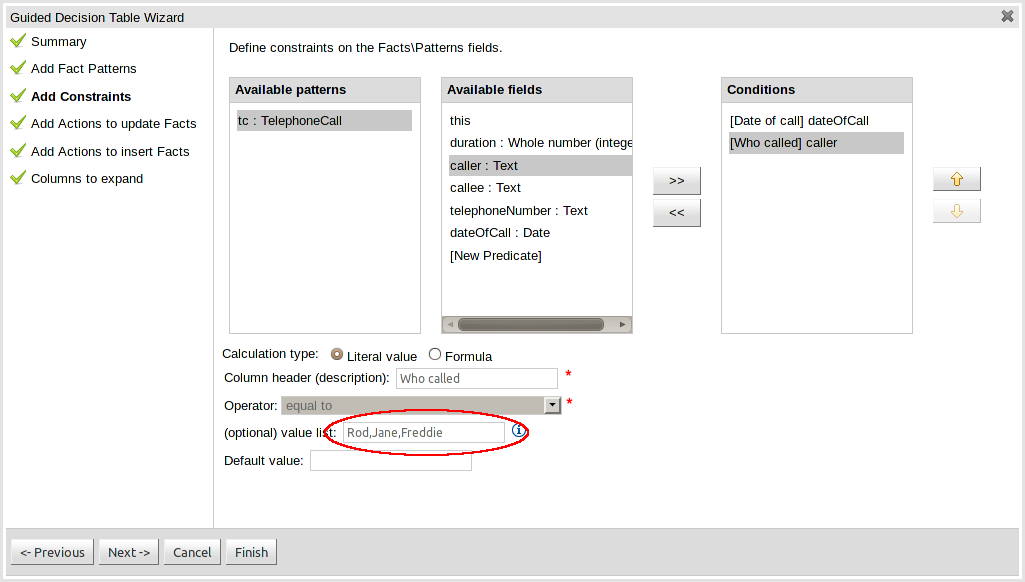
This page allows field constraints on the Fact types you have chosen to use in the decision table to be defined. Fact types chosen on the previous Wizard page are listed in the right-hand listbox. Selecting a Fact type by clicking on it will result in a list of available fields being shown in the middle listbox together with an option to create a predicate that do not require a specific field. Fields can be added to the pattern's constraints by clicking on the field and then the ">>" button. Fields can be removed from the pattern definition by clicking on the Condition in the right-hand listbox and then the "<<" button. All fields need to have a column header and operator. Incomplete fields will be highlighted and a warning message displayed. You will be unable to finish your definition until all warnings have been resolved.
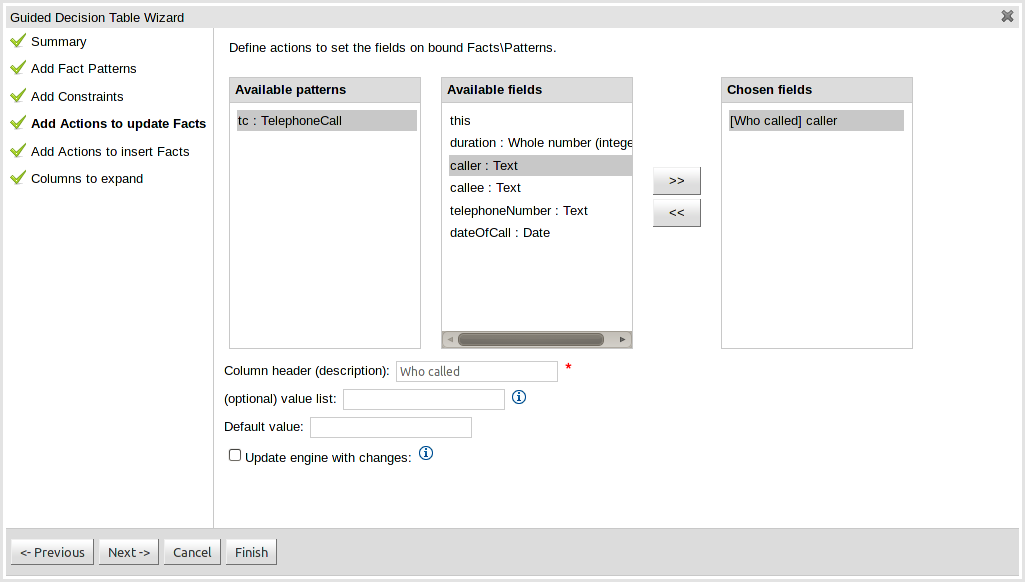
Fact types that have been defined can be updated in the consequence, or action, part of a rule. This page allows such actions to be defined. Fact types added to the decision table definition are listed in the left-hand listbox. Selecting a Fact type by clicking on it will result in a list of available fields being shown in the middle listbox. Fields that need to be updated by the rule can be added by selecting an available field and pressing the ">>" button. Fields can be removed similarly by clicking on a chosen field and then the "<<" button. All actions require a column header. Any incomplete actions will be highlighted and a warning message displayed. You will be unable to finish your definition until all warnings have been resolved.
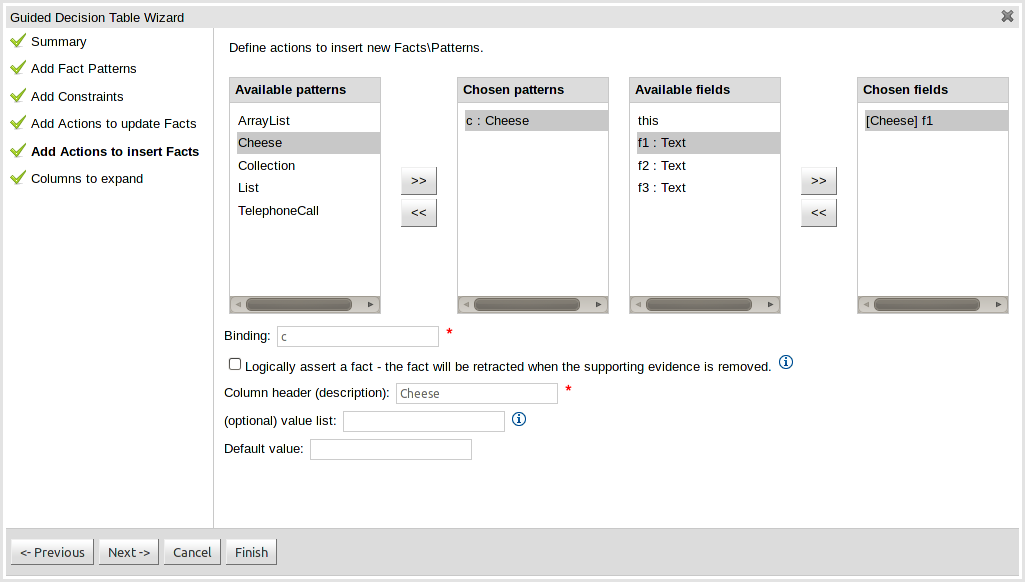
Actions can also be defined to insert new Facts into the Rule Engine. A list of Fact types available in your model are listed in the left-hand listbox. Select those you wish to include in your decision table definition by clicking on them and pressing the ">>" button between the left most listbox and that titled "Chosen patterns". Removal is a similar process whereby a chosen pattern can be selected and removed by pressing the "<<" button. Selection of a chosen pattern presents the user with a list of available fields. Fields that need to have values set by the action can be added by selecting them and pressing the ">>" button between the "Available fields" and "Chosen fields" listbox. Removal is a similar process as already described. New Facts need to be bound to a variable and have a column heading specified. Incomplete Facts and\or fields will be highlighted and a warning message displayed. You will be unable to finish your definition until all warnings have been resolved.
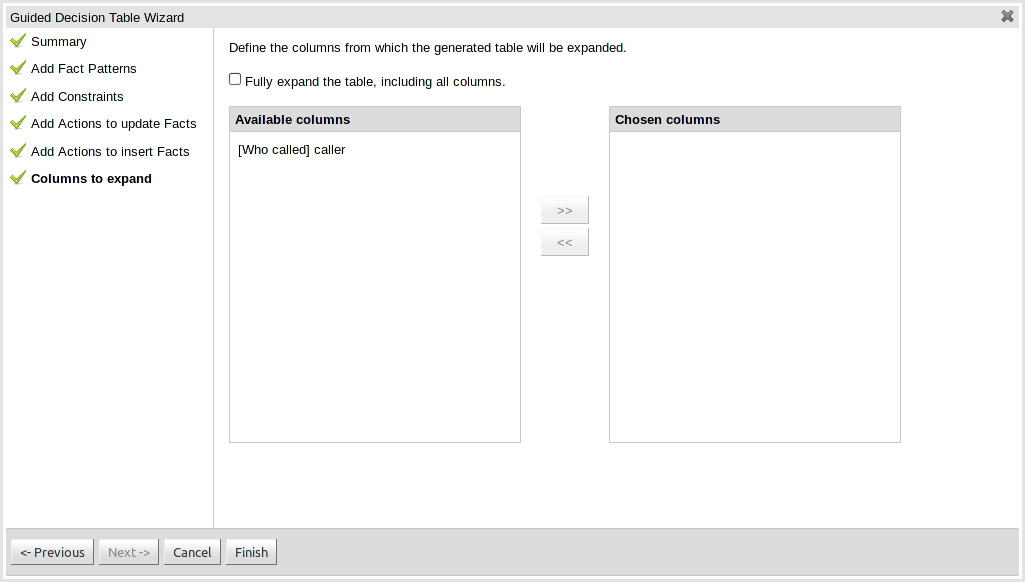
This page controls how the decision table, based upon Conditions defined on the prior pages, will be created. Condition columns defined with an optional list of permitted values can be used to create rows in the decision table. Where a number of Condition columns have been defined with lists of permitted values the resulting table will contain a row for every combination of values; i.e. the decision table will be in expanded form. By default all Condition columns defined with value lists will be included in the expansion however you are able to select a sub-set of columns if so required. This can be accomplished by unticking the "Fully expand" checkbox and adding columns to the right-hand listbox. If no expansion is required untick the "Fully expand" checkbox and ensure zero columns are added to the right-hand listbox.
This section allows individual rules to be defined using the columns defined earlier.
Rows can be appended to the end of the table by selecting the "Add Row" button. Rows can also be inserted by clicking the "+" icon beside an existing row. The "-" icon can be used to delete rows.
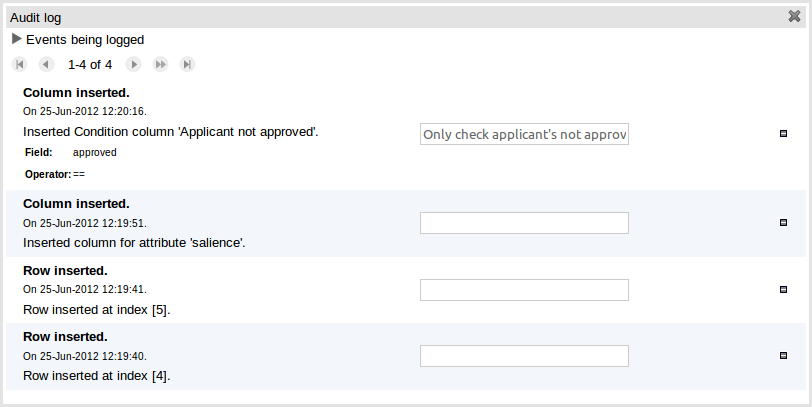
An audit log has been added to the web-guided Decision Table editor to track additions, deletions and modifications.
By default the audit log is not configured to record any events, however, users can easily select the events in which they are interested.
The audit log is persisted whenever the asset is checked in.
Once the capture of events has been enabled all susbsequent operations are recorded. Users are able to perform the following:-
Record an explanatory note beside each event.
Delete an event from the log. Event details remain in the underlying repository.
The guided rule editor is great when you need to define a single rule, however if you need to define multiple rules following the same structure but with different values in field constraints or action sections a "Rule Template" is a valuable asset. Rule templates allow the user to define a rule structure with place-holders for values that are to be interpolated from a table of data. Literal values, formulae and expressions can also continue to be used.
Rule Templates can often be used as an alternative for Decision Tables in Drools Guvnor.
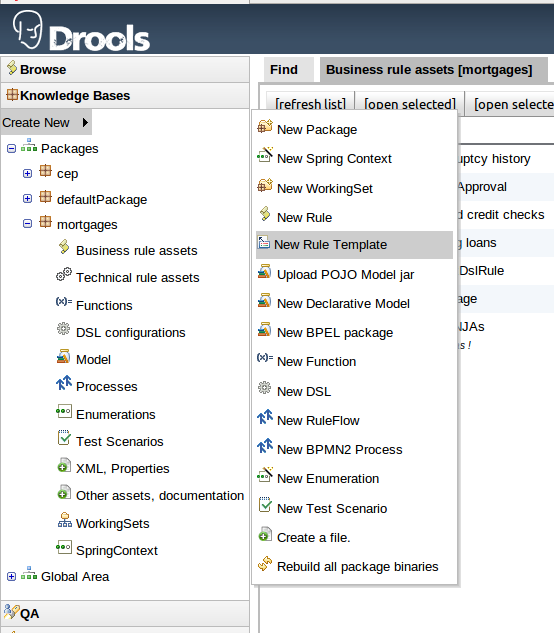
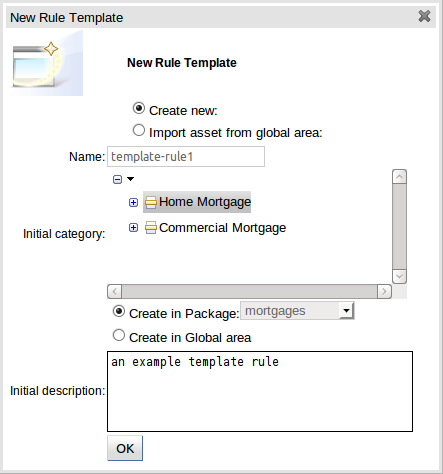
To create a template for a rule simply select the "New Rule Template" from the Knowledge Bases "Create New" popup menu. The create "New Rule Template" asset popup window will appear from which the normal asset attributes can be defined; such as name, category and description.
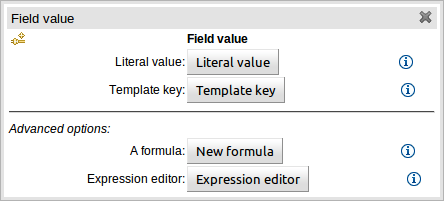
Once a rule template has been created the editor is displayed. The editor takes the form of the standard guided editor explained in more detail under the "Rule Authoring" section. As the rule is constructed you are given the ability to insert "Template Keys" as place-holders within your field constraints and action sections. Literal values, formulae and expressions can continue to be used as in the standard guided editor.
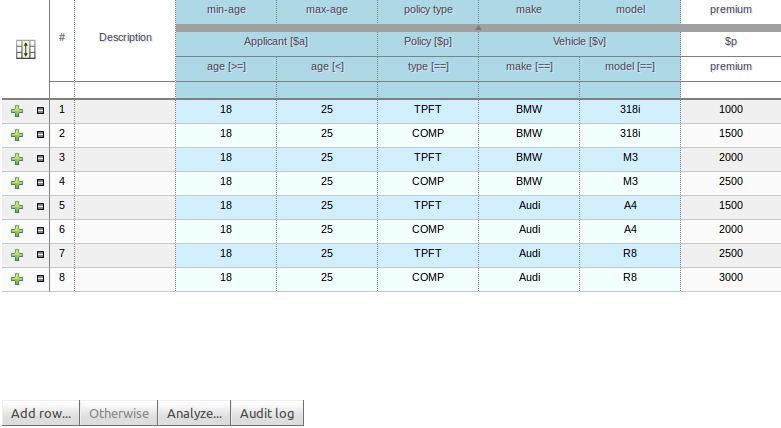
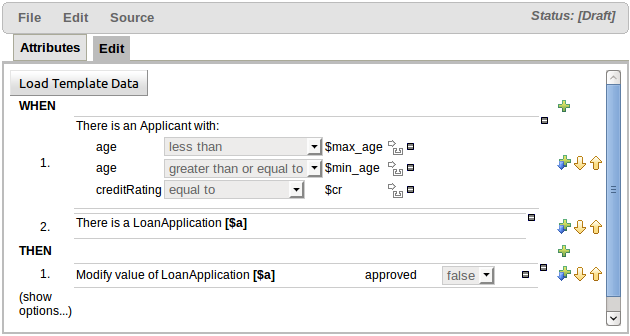
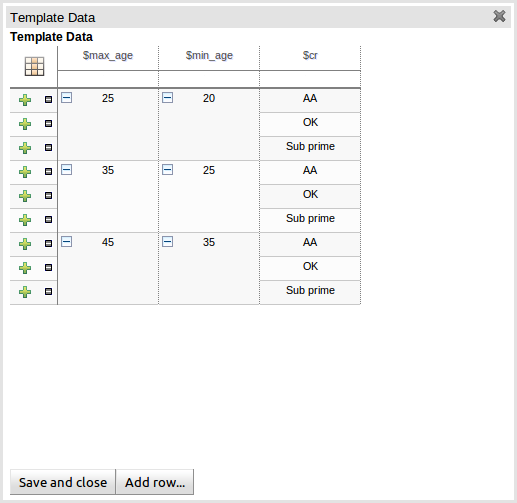
The following screenshot illustrates a simple rule that has been defined with a "Template Key" for the applicants' maximum age, minimum age and credit rating. The template keys have been defined as "$max_age", "$min_age" and "$cr" respectively.
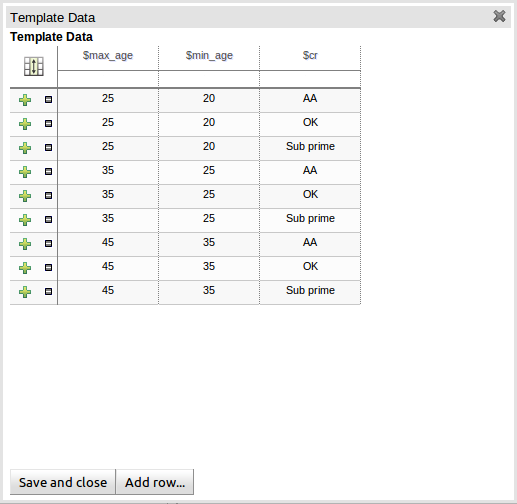
When you have completed the definition of your rule template you need to enter the data that will be used to interpolate the "Template Key" place-holders. Drools Guvnor provides the facility to enter data in a flexible grid within the guided editor screen. The grid editor can be launched by pressing the "Load Template Data" button on the guided editor screen.
The rule template data grid is very flexible; with different pop-up editors for the underlying fields' data-types. Columns can be resized and sorted; and cells can be merged and grouped to facilitate rapid data entry.
One row of data interpolates the "Template Key" place-holders for a single rule; thus one row becomes one rule.
Note
If any cells for a row are left blank a rule for the applicable row is not generated.
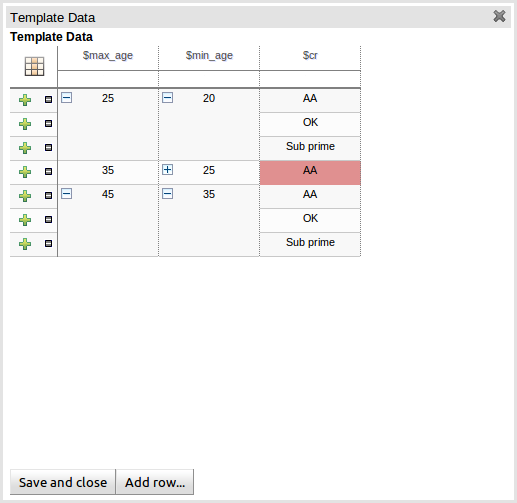
The icon in the top left of the grid toggles cell merging on and off. When cells are merged those in the same column with identical values are merged into a single cell. This simplifies changing the value of multiple cells that shared the same original value. When cells are merged they also gain an icon in the top-left of the cell that allows rows spanning the merged cell to be grouped.
Cells that have been merged can be further collapsed into a single row. Clicking the [+\-] icon in the top left of a merged cell collapses the corresponding rows into a single entry. Cells in other columns spanning the collapsed rows that have identical values are shown unchanged. Cells in other columns spanning the collapsed rows that have different values are highlighted and the first value displayed.
When the value of a grouped cell is altered all cells that have been collapsed also have their values updated.
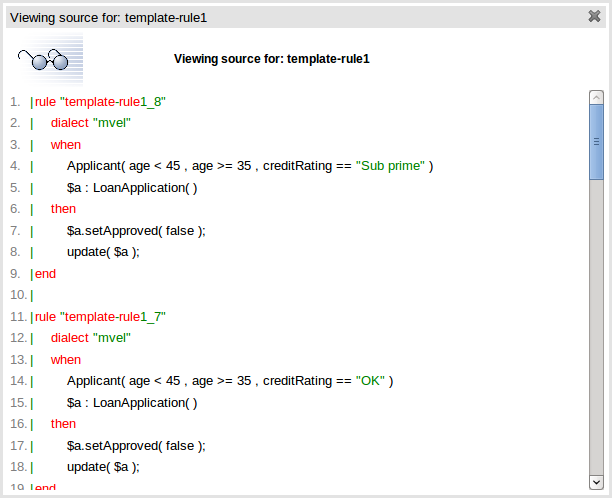
Whilst not necessary, rule authors can view the DRL that will be generated for a "Rule Template" and associated data. This feature and its operation is no different to that for other assets. Select the "Source" -> "View Source" menu item from the Asset Editor screen. The DRL for all rules will be displayed.
For any rule base application, a fact model is needed to drive the rules. The fact model typically overlaps with the applications domain model, but in general it will be decoupled from it (as it makes the rules easier to manage over time). There are no technical limitations on using your domain model as your fact model, however this introduces tighter coupling between your business domain (domain model) and your knowledge domain (fact model). Consequentially if your domain model were to change you would need to, at the very least, revisit your rule definitions.
There are two ways to do define your fact model; each of which will be discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Upload a JAR file containing Java Classes used by both your application and rules.
Declare a model within Guvnor; that can be exported as a KnowledgeBase and used within your Java code.
Creating and uploading a JAR model file is a two step process.
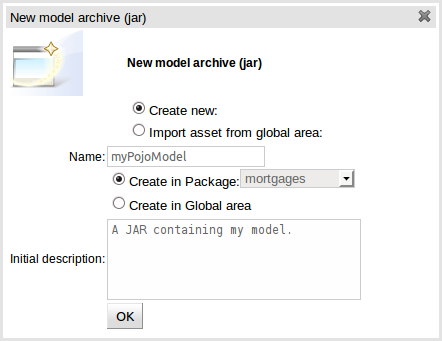
Select "Upload POJO Model JAR" from the "Create New" popup menu from the "Knowledge Bases" section of the Explorer widget. This will launch the "New Asset" configuration screen from which the new upload can be given basic details such as name, category and a description.
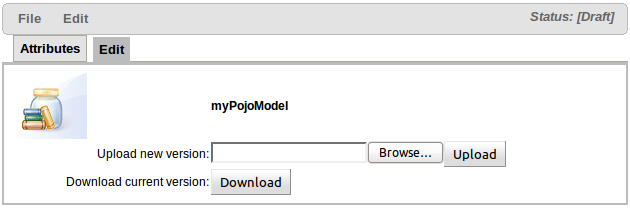
Once the POJO Model JAR asset has been created you are presented with a screen to upload the actual JAR containing the model defined as Java classes and packaged in a regular Java JAR file. Many Java IDE's are able to export classes as a JAR file.
Why would you chose declared types over JAR files: generally this reinforces the fact that the model "belongs" to the KnowledgeBase, rather then the application, and allows the model to have a lifecycle separate from the application. It also allows Java types to be enriched with Rule specific annotations. Additionally it also removes the burden of keeping JAR files synchronised between rules and the applications that use the rules.
Declarative models can be either:-
A standalone definition of the entire Fact model used within your rules.
Supplementary Fact definitions to support a Java POJO Model.
Used to enrich a Java JAR model as uploaded in the previous section. Enriching JAR models allows annotations used by Drools (such as a "role" of type "event" for Facts used as events in Complex Event Processing) to be appended to classes. When enriching an existing Java JAR model the package name in Guvnor needs to be identical to the Java package name containing the class(es) you wish to enrich.
Creating a Declarative Model is a two step process.
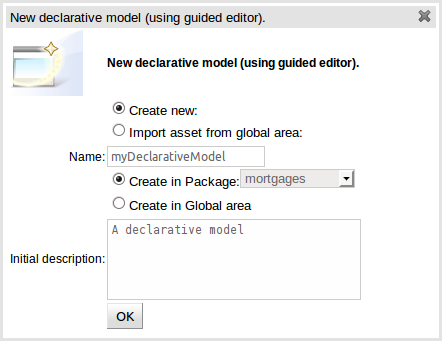
Select "New Declarative Model" from the "Create New" popup menu from the "Knowledge Bases" section of the Explorer widget. This will launch the "New Asset" configuration screen from which the new upload can be given basic details such as name, category and a description.
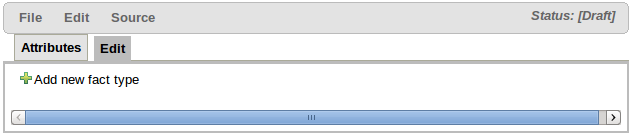
Once the Declarative Model asset has been created you are presented with the initial modelling screen; that is empty to begin.
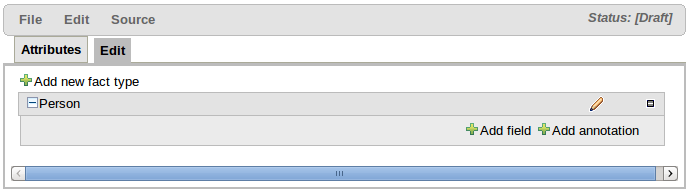
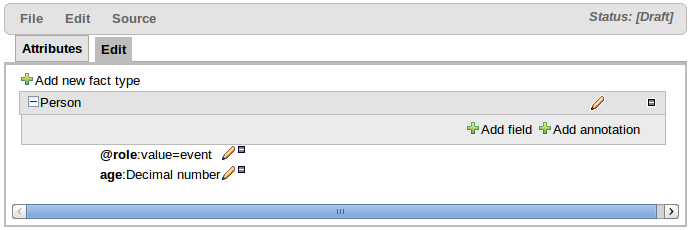
Facts, being semantically equivalent to Java classes, can be created by selecting the "Add new fact type" button. An existing Fact definition can be edited by clicking the "pencil" icon on the same row as the Fact name. Furthermore existing Facts can be deleted by clicking the "[-]" icon.
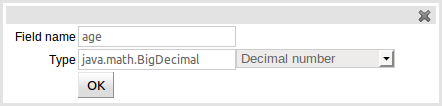
Fact Fields can be created by selecting the "Add field" button. The type of a field is suggested by a list (but this list is not exhaustive). An existing Fact Field definition can be edited by clicking the "pencil" icon on the same row as the Fact Field name. Furthermore existing Fact Fields can be deleted by clicking the "[-]" icon.
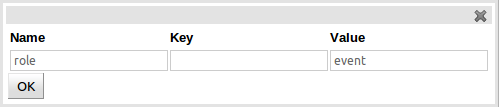
Fact annotations can be created by selecting the "Add annotation" button. Annotations are listed under the Fact title, before the fields, by convention. Annotations are prefixed with the "@" symbol. This not only makes them instantly recognisable but is also consistent with their definition in DRL.
The annotation "Name" and "Value" are mandatory whereas the "Key" is optional. If a "Key" is not given a default value of "value" will be assigned. This is consistent with how annotations are held within Drools Expert.
An existing Fact Annotation can be edited by clicking the "pencil" icon on the same row as the Fact Annotation name. Furthermore existing Fact Annotations can be deleted by clicking the "[-]" icon.
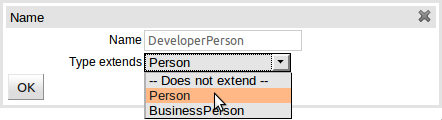
Declarative types can extend existing:-
Java classes uploaded as part of a JAR (POJO) model
Other declared types in the same package.
To extend a Java class the following steps need to be completed:-
Import the applicable Java JAR into Guvnor
If the Java package name in which the class belongs is different to the Guvnor package name in to which the JAR has been imported ensure the Guvnor package imports the class from which you want to extend. This is normally completed for you automatically when you upload a JAR model however if you have multiple classes with the same name in the JAR you should check the appropriate one has been imported.
Within the Declarative Modelling screen define an empty type (i.e. with no fields) of the same name as that you want to extend.
Create a new declarative type as appropriate, extending the empty declaration created in the preceding step.
Note
Only properties on Java classes that have both a "getter" and "setter" following standard Java Bean conventions are available on the declared sub-type. This is because the declarative semantics imply all properties on declared types have both accessors and mutators.
Declared types are generated at knowledge base compilation time, i.e. the application will only have access to them at application run time. Therefore, these classes are not available for direct reference from the application.
Declarative types can be used like normal fact objects, but the way you create them is different (as they are not on your applications classpath). To create these objects, they are available from the KnowledgeBase instance.
Example 4.1. Handling declared fact types through the API
// get a reference to a knowledge base with a declared type:
KnowledgeBase kbase = ...
// get the declared FactType
FactType personType = kbase.getFactType( "org.drools.examples",
"Person" );
// handle the type as necessary:
// create instances:
Object bob = personType.newInstance();
// set attributes values
personType.set( bob,
"name",
"Bob" );
personType.set( bob,
"age",
42 );
// insert fact into a session
StatefulKnowledgeSession ksession = ...
ksession.insert( bob );
ksession.fireAllRules();
// read attributes
String name = personType.get( bob, "name" );
int age = personType.get( bob, "age" );Note
The namespace of the declared type is the package namespace
where it was declared (i.e. org.drools.examples in the
above example).
Functions are another asset type. They are NOT rules, and should only be used when necessary. The function editor is a textual editor. Functions
The DSL editor allows DSL Sentences to be authored. The reader should take time to explore DSL features in the Drools Expert documentation; as the syntax in Guvnor's DSL Editor is identical. The normal syntax is extended to provide "hints" to control how the DSL variable is rendered and validated within the user-interface.
The following "hints" are supported:-
{<varName>:<regular expression>}
This will render a text field in place of the DSL variable when the DSL Sentence is used in the guided editor. The content of the text field will be validated against the regular expression.
{<varName>:ENUM:<factType.fieldName>}
This will render an enumeration in place of the DSL variable when the DSL Sentence is used in the guided editor. <factType.fieldName> binds the enumeration to the model Fact and Field enumeration definition. This could be either a "Guvnor enumeration" (i.e. defined as a Knowledge Base "Enumeration") or a Java enumeration (i.e. defined in a model POJO JAR file).
{<varName>:DATE:<dateFormat>}
This will render a Date selector in place of the DSL variable when the DSL Sentence is used in the guided editor.
{<varName>:BOOLEAN:<[checked | unchecked]>}
This will render a dropdown selector in place of the DSL variable, providing boolean choices, when the DSL Sentence is used in the guided editor.
{<varName>:CF:<factType.fieldName>}
This will render a button that will allow you to set the value of this variable using a Custom Form. In order to use this feature, a Working-Set containing a Custom Form Configuration for factType.fieldName must be active. If there is no such Working-Set, a simple text box is used (just like a regular variable).
For more information, please read more about Working-Sets and Custom Form Configurations.
Rule flows: Rule flows allow you to visually describe the steps
taken - so not all rules are evaluated at once, but there is a flow of
logic. Rule flows are not covered in this chapter on the Guvnor, but you
can use the IDE to graphically draw ruleflows, and upload the
.rfm file to the Guvnor.
Similar to spreadsheets, you upload/download ruleflow files (the eclipse IDE has a graphical editor for them). The details of Rule Flows are not discussed here.
Data enumerations are an optional asset type that technical folk can configure to provide drop down lists for the guided editor. These are stored and edited just like any other asset, and apply to the package that they belong to.
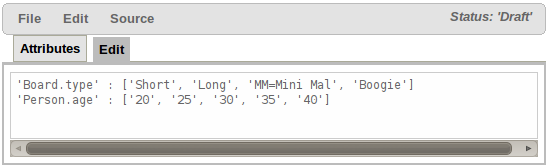
The contents of an enum config are a mapping of Fact.field to a list of values to be used in a drop down. That list can either be literal, or use a utility class (which you put on the classpath) to load a list of strings. The strings are either a value to be shown on a drop down, or a mapping from the code value (what ends up used in the rule) and a display value (see the example below, using the '=').
In the above diagram - the "MM" indicates a value that will be used in the rule, yet "Mini Mal" will be displayed in the GUI.
Getting data lists from external data sources: It is possible to have
the Guvnor call a piece of code which will load a list of Strings. To do
this, you will need a bit of code that returns a java.util.List
(of String's) to be on the classpath of the Guvnor. Instead of specifying a
list of values in the Guvnor itself - the code can return the list of
Strings (you can use the "=" inside the strings if you want to use a
different display value to the rule value, as normal). For example, in the
'Person.age' line above, you could change it to:
'Person.age' : (new com.yourco.DataHelper()).getListOfAges()
This assumes you have a class called "DataHelper" which has a method "getListOfAges()" which returns a List of strings (and is on the classpath). You can of course mix these "dynamic" enumerations with fixed lists. You could for example load from a database using JDBC. The data enumerations are loaded the first time you use the guided editor in a session. If you have any guided editor sessions open - you will need to close and then open the rule to see the change. To check the enumeration is loaded - if you go to the Package configuration screen, you can "save and validate" the package - this will check it and provide any error feedback.
There are a few other advanced things you can do with data enumerations.
Drop down lists that depend on field values: Lets imagine a simple fact model, we have a class called Vehicle, which has 2 fields: "engineType" and "fuelType". We want to have a choice for the "engineType" of "Petrol" or "Diesel". Now, obviously the choice type for fuel must be dependent on the engine type (so for Petrol we have ULP and PULP, and for Diesel we have BIO and NORMAL). We can express this dependency in an enumeration as:
'Vehicle.engineType' : ['Petrol', 'Diesel'] 'Vehicle.fuelType[engineType=Petrol]' : ['ULP', 'PULP' ] 'Vehicle.fuelType[engineType=Diesel]' : ['BIO', 'NORMAL' ]
This shows how it is possible to make the choices dependent on other field values. Note that once you pick the engineType, the choice list for the fuelType will be determined.
Loading enums programmatically: In some cases, people may want to
load their enumeration data entirely from external data source (such as a
relational database). To do this, you can implement a class that returns a
Map. The key of the map is a string (which is the Fact.field name as shown
above), and the value is a java.util.List of Strings.
public class SampleDataSource2 {
public Map<String>, List<String> loadData() {
Map data = new HashMap();
List d = new ArrayList();
d.add("value1");
d.add("value2");
data.put("Fact.field", d);
return data;
}
}
And in the enumeration in the BRMS, you put:
=(new SampleDataSource2()).loadData()
The "=" tells it to load the data by executing your code.
Mode advanced enumerations: In the above cases, the values in the lists are calculated up front. This is fine for relatively static data, or small amounts of data. Imagine a scenario where you have lists of countries, each country has a list of states, each state has a list of localities, each locality has a list of streets and so on... You can see how this is a lot of data, and it can not be loaded up. The lists should be loaded dependent on what country was selected etc...
Well the above can be addressed in the following fashion:
'Fact.field[dependentField1, dependentField2]' : '(new com.yourco.DataHelper()).getListOfAges("@{dependentField1}", "@{dependentField2}")'Similar to above, but note that we have just specified what fields are needed, and also on the right of the ":" there are quotes around the expression. This expression will then be evaluated, only when needed, substituting the values from the fields specified. This means you can use the field values from the GUI to drive a database query, and drill down into data etc. When the drop down is loaded, or the rule loaded, it will refresh the list based on the fields. 'dependentField1' and 'dependentField2' are names of fields on the 'Fact' type - these are used to calculate the list of values which will be shown in a drop down if values for the "field".
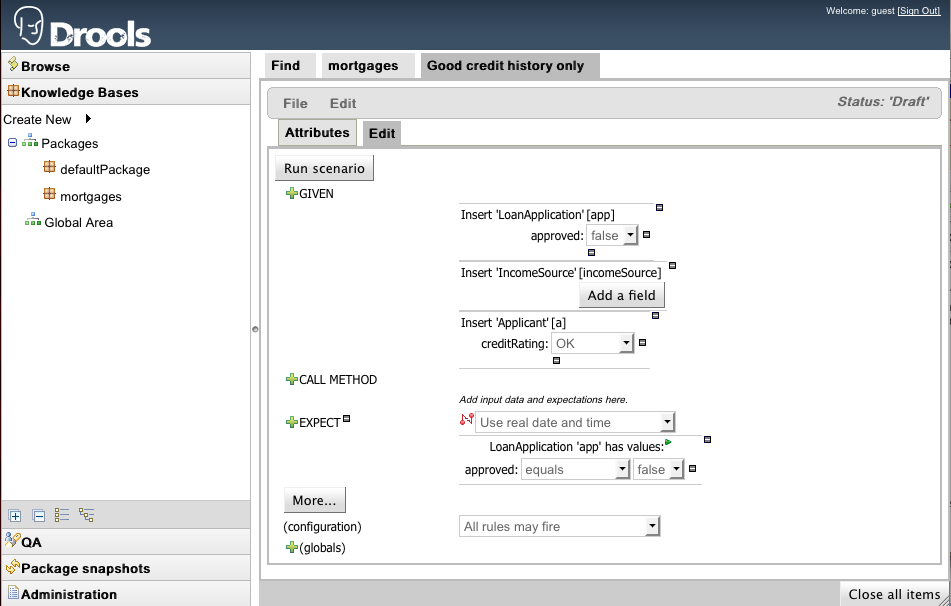
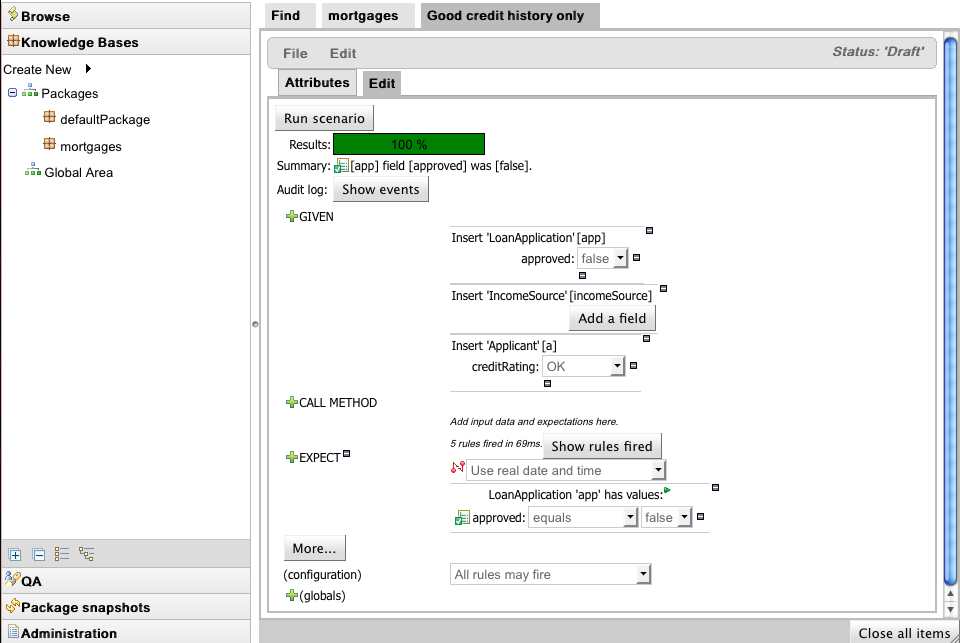
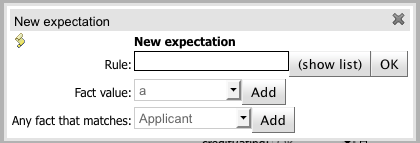
Test Scenarios are used to validate that rules and knowledge base work as expected. When the knowledge base evolves, Test Scenarios guard against regression.
Given section lists the facts needed for the behaviour. Expect section lists the expected changes and actions done by the behaviour. Given facts are passed for the Test Scenario before execution. During the rule execution, changes in the knowledge base are recorded. After the execution ends the recorded actions, existing facts in the knowledge base and knowledge base output is compared against the expectations.
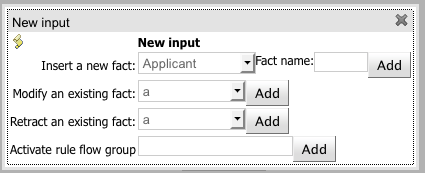
Insert a new fact - Adds a new fact that will be inserted into the knowledge base before execution.
Modify an existing fact - Allows editing a fact between knowledge base executions.
Retract an existing fact - Allows removing facts between executions.
Activate rule flow group - Allows rules from a rule flow group to be tested, by activating the group in advance.
Rule - Validate that a certain rule fired.
Fact value - Validate fact values for a fact created in the Given section.
Any fact that matches - Validate that there is at least one fact in the knowledge base with the specified field values.
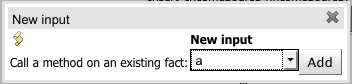
Call method on an existing fact - Call a method from a fact in the beginning of the rule execution.
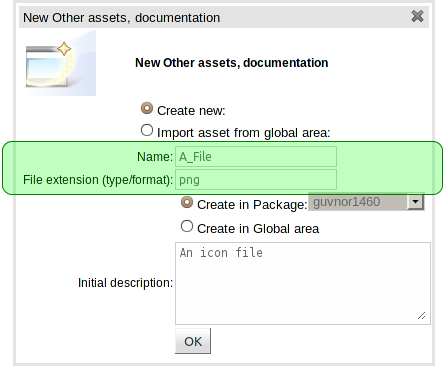
Files can be stored in Guvnor as assets.
You need to provide the asset name and file extension in the "New Asset" popup dialog.
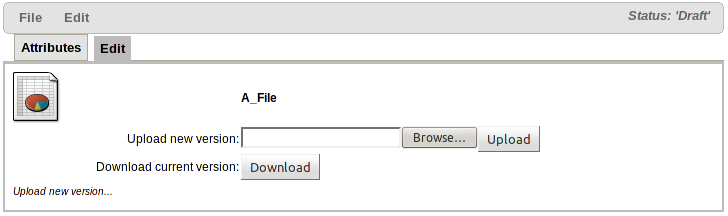
Once you have created the asset a screen to upload (or download) the file itself is shown.
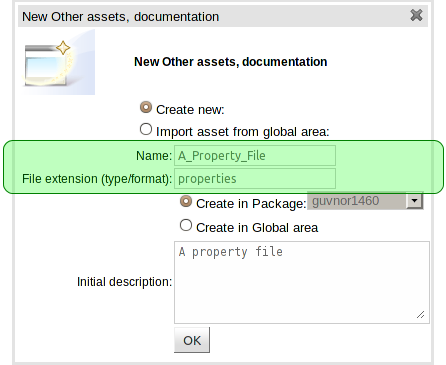
If you specify a file extension of "properties" a standard Java properties file can also be created.
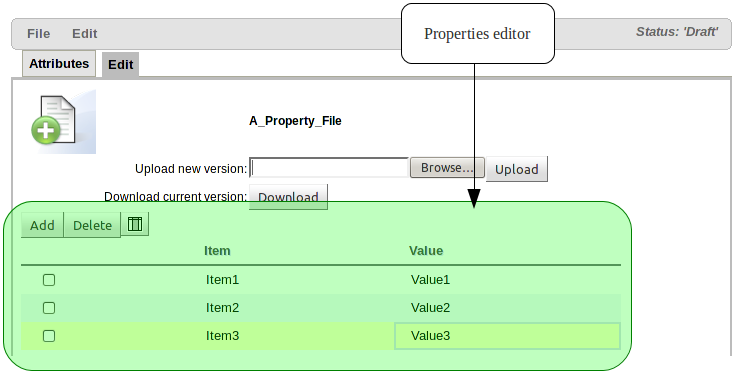
The properties name\value pairs can be maintained from within Guvnor.
Change-set is one of the ways Drools has to group one or more Assets in a single Asset. Change-sets can then be added to a Knowledge Builder or a Knowledge Agent to process all the assets referenced by it.
By default, Guvnor provides a unique Change-Set per package containing the package binary or the drl source. The main problem with this is when you want to use just a sub-set of assets of a package (or even from different packages) in your application.
Using the Change-Set editor you can define your own change-sets inside Guvnor in any way you want. You could have a combination of different assets and packages, or even different snapshots of a package in a change-set. You can have all the change-sets per package you need, so if different applications are using the same package in different ways (different assets or assets' versions of a same package) you can make use of this feature of Guvnor.
To create a new Chang-Set you have to go to "Create New" -> "New Change Set" option in Knowledge Base section of Guvnor.
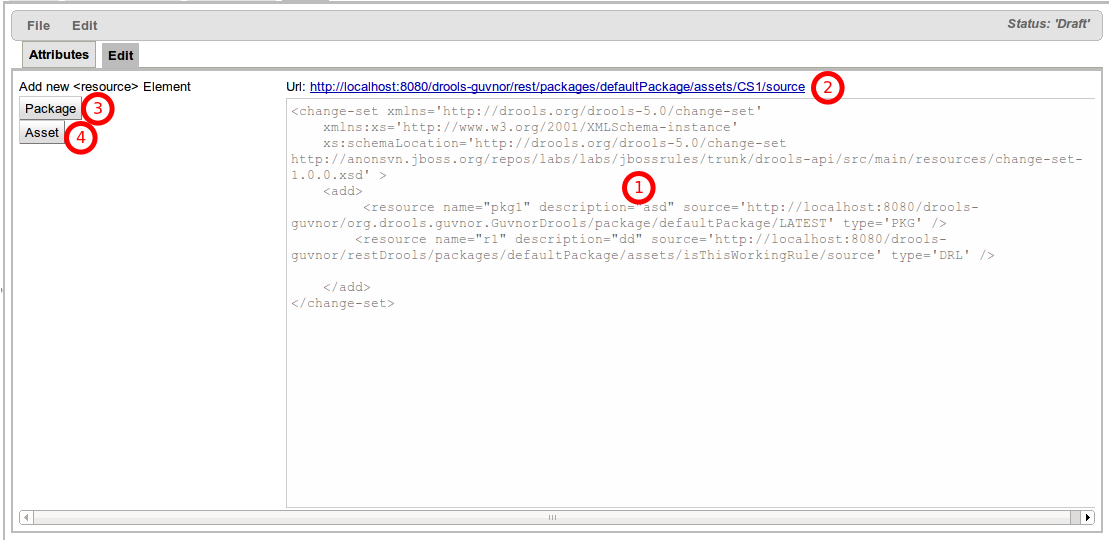
In the editor you have 4 items you can interact with:
Change-Set Editor canvas: Here you can edit your change-set by hand. You can add, remove or edit resources as you wish. Of course you will need to know the URL of each of the resources. You could get this information from the "Attributes" tab of each of the resources.
Change-Set URL: This is the URL you need to use in your applications to make reference to this change-set.
Package Button: This is an easy way to add packages to your change-set. You need to place the cursor where you want to add a new Package in the Change-Set Editor canvas and then click this button. A Wizard will appear to help you choose the right package. See next section for further information.
Asset Button: Useful button to add a new Assets to the Change-Set using a Wizard. For more information please read "Adding Assets using a Wizard" section.
Clicking in the "Package" button of Change-Set Editor, a wizard will be displayed to help you choose the package you want to add as resource.
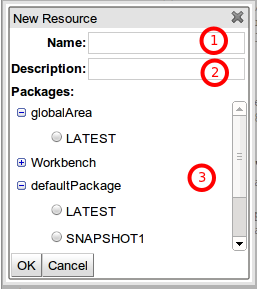
The Package Wizard has 3 sections:
Name: Each resource inside a Change-Set could have a descriptive name. Use this optional field to set this property.
Description: Each resource inside a Change-Set could have a description. Use this optional field to set this property.
Packages: In this section you can select the package and the Snapshot version of a package you want to add as a resource of the Change-Set you are editing. If the Change-Set you are editing belongs to the Global Area, then you will be able to select the resource to add from all the packages defined in Guvnor and their snapshots of course. If the Change-Set you are editing belongs to a particular Package, you will only see the Snapshots of that package in this Wizard.
You have 2 ways of adding assets as resources of a Change-Set: by hand using the Change-Set Editor canvas or using the Asset Wizard. This Wizard is invoked using the "Asset" button of the editor.
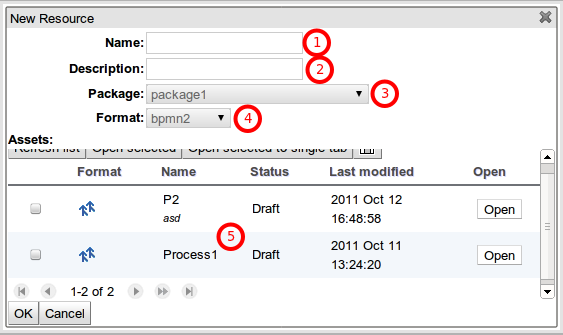
This Wizard has 5 sections:
Name: Each resource inside a Change-Set could have a descriptive name. Use this optional field to set this property.
Description: Each resource inside a Change-Set could have a description. Use this optional field to set this property.
Package: Use this field to filter the assets of a particular Package. If the Change-Set you are editing belongs to the Global Area, then you will be able to select any package, otherwise the package where your Change-Set belongs is automatically selected and you will not be able to change it.
Format: Use this field to filter the type of assets you are looking for.
Assets: The list of assets that match the selected package and format. You can select one or more assets using the check-box column and then click "OK" to add each resource to the Change-Set you are editing.
Service Config is a special asset that defines an execution service configuration. This execution service is a war file (generated automatically by the editor) which you can deploy to execute KnowledgeBases remotely for any sort of client application. As this service is stateless, it is possible to have as many of these services deployed as you need to serve the client load.
This version of the execution server supports as many Knowledge Bases as you need, supporting also multiple stateless and stateful sessions in a native way.
To create a new Service you have to go to "Create New" -> "New Service Config" option in Knowledge Base section of Guvnor. In the following sections you have detailed information on how to configure your Service Config.
As already mentioned the Service editor allows users configure as many knowledge bases as they need. This section describes how to use the tabbed panel to configure your Service with multiple knowledge bases.
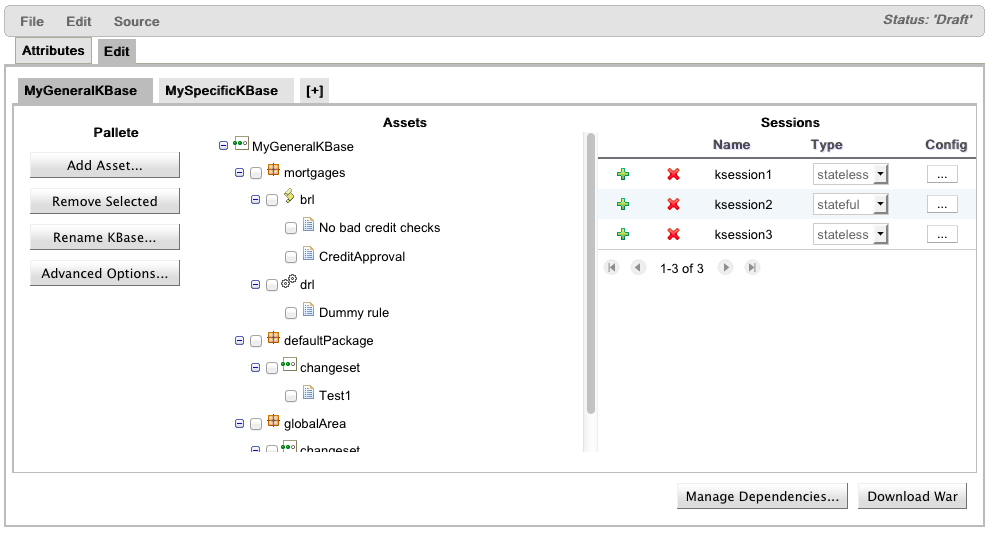
The above panel is composed by the following:
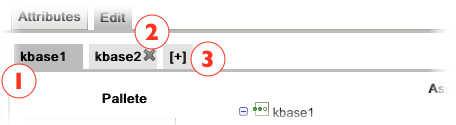
Named Tab: each tab represents a knowledge base, and once selected, its configuration panel is displayed. See next section for further information.
Removing: in order to remove an existing tab/knowledge base, you have to click the highlighted "X" and then confirm the action. Important to note that should exists at least one knowledge base.
Add new: to add a new kbase, all you need is click on this special tab. The new kbase will be added on the left hand side of the plus tab.
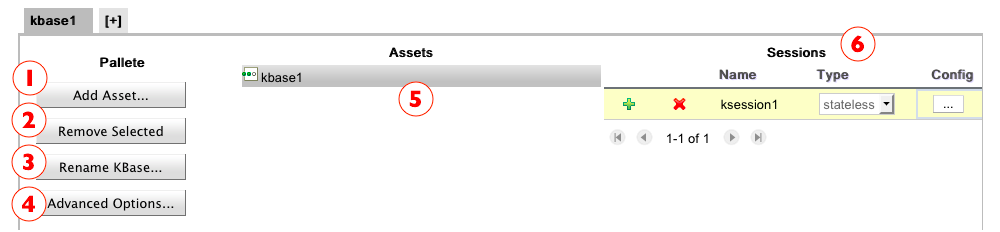
In the above configuration panel you have 6 items that you can interact with:
Add Asset Button: add new assets to the tree using a wizard. See next section for further information.
Remove Selected Button: remove the selected assets (the ones that are checked) from Assets Tree.
Rename KBase Button: this button will open a standard “prompt for rename” dialog box.
Advanced Options Button: opens the advanced knowledge base configuration dialog. Configurations that are not available in the panel, should be available in this advanced dialog. Detailed information about it can be found in the "Advanced Knowledge Base Configuration Options" section.
Assets Tree: Here you have the complete set of assets, grouped by package and type, that are referenced by the active knowledge base configuration. For additional information, please read the "Assets Tree" section.
Sessions Grid: Here users can create, delete and edit in place a list of desires ksessions. For detailed instructions on how to configure ksessions, please check the "Configuring Knowledge Sessions" section.
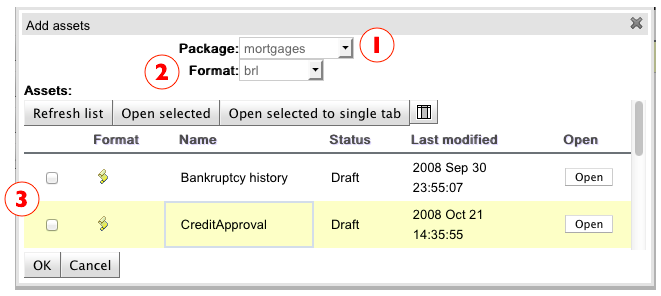
This Wizard has 3 sections:
Package: Use this field to filter the assets of a particular Package. By default the selected package is the one that your Service belongs to, but you're not limited to it as you can select any other package that you want.
Format: Use this field to filter the type of assets you are looking for.
Assets: The list of assets that match the selected package and format. You can select one or more assets using the check-box column and then click "OK" to add each resource to the Assets Tree of your active knowledge base configuration.
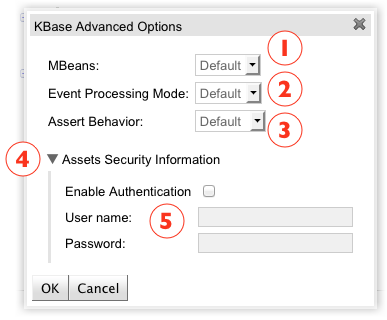
This dialog has the following sections:
MBeans: Can enable or disable MBeans on active knowledge base. Users can also keep the default engine behavior by choosing the Default option.
Event Processing Mode: Defines the event processing mode, which options are Cloud or Stream. Users can also keep the default engine behavior by choosing the Default option. For more information about Event Processing Mode, consult the Drools Fusion documentation.
Assert Behavior: Defines the expected assert behavior, which options are Identity and Equality. Users can also keep the default engine behavior by choosing the Default option.
Assets Security Information: This section holds any security related configuration to remotely access the guvnor repository.
Enable Authentication, User name and Password: If explicit authentication is enabled, you should provide the user name and password for remote access.
The assets tree is composed by 4 different types of nodes:
Knowledge Base: Root node that represents the active kbase.
Packages: Selected assets are grouped by its packages. Important to note that those packages are just informative and are not relevant for the service runtime.
Asset Types: Groups assets of the same package by type. The actual list of supported types are: brl, drl, dsl, bpmn2, gdst, changeset and jars.
Assets: Selected assets of a given type (parent) and package (grandparent).
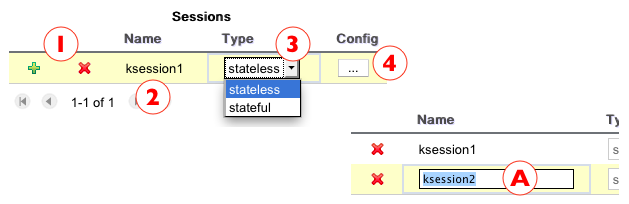
Figure 4.102. Knowledge Sessions Grid - basic information to define a ksession are available to be edited in place.
The ksessions grid is composed by the following columns:
Add and Remove Icons: Users can use these icons to add new or remove existing knowledge sessions. Important to note that should exists at least one knowledge session.
Knowledge Session Name: Defines the ksession name. Users can edit this particular field in place as highlighted on box "A".
Session Type: Defines if a ksession is Stateless or Stateful. Users can also select the desired type directly on the grid.
Configuration Button: This button opens the knowledge session configuration dialog. See next section for further information.
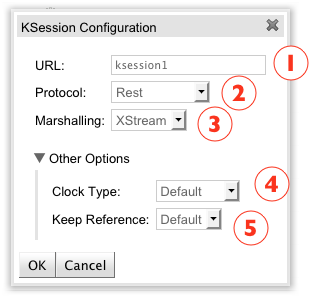
This ksession configuration dialog has the following 5 fields:
URL: Defines a custom URL to access the active ksession.
Protocol: Defines the protocol that ksession should be accessed by, default options is REST.
Marshalling: Defines which marshalling technology should be used, default option is XStream.
Clock Type: Defines the type of the session clock, which options are Pseudo or Real Time. Users can also keep the default engine behavior by choosing the Default option.
Keep Reference: Enable or disable the engine to keep a weak reference of this section on the kbase. Users can also use the default engine behavior by choosing the Default option.
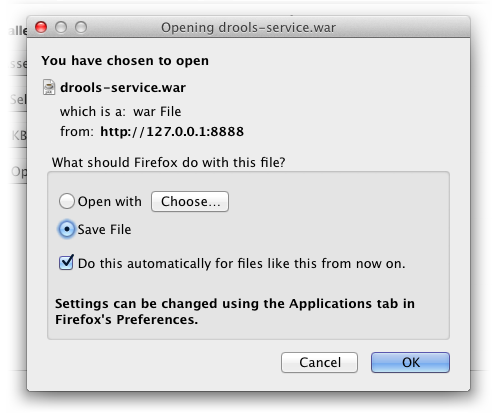
After configuring your knowledge bases and sessions, you're ready to download the service war. For so, all you need to do is click on the "Download War" button and the following screen (or a similar one, depending on your browser) will show up.
Warning
Before click on the "Download War" button, makes sure that you don't have pending changes. This is a very important step, once the the war file is generated based on the latest saved information and not on the current screen state.
The generated file is a ready to be deployed war file. Which mean that it contains all the necessary configuration files and all the needed dependencies as well. As dependency management is a crucial subject in a real world applications deployment, we will discuss that in more detail in the next section.
As already mentioned, the generated war file contains all the necessary dependencies to execute the configured Service, it works seamlessly on most standard containers.
But the reality is a bit different, rarely you'll have a "standard container", usually what you have is an already configured and running container. Probably this container even have already configured a set of shared libs between your deployed application. And, of course, you don't want those shared libs on your wars.
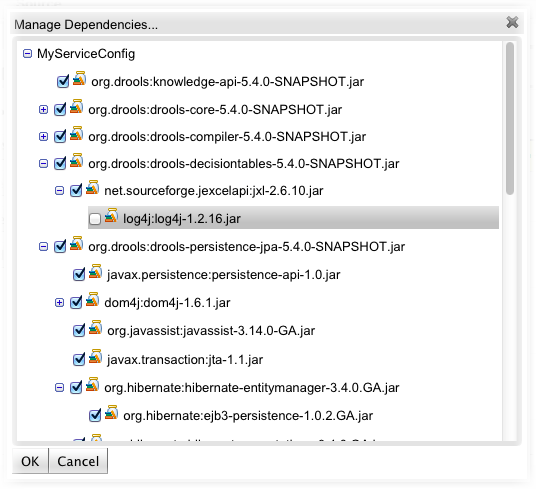
Based on real world scenarios, we made available a simple dependency management tool, that enables you explore and configure all the dependencies contained in the generated war file. This tool can be accessed just by clicking the "Manage Dependencies" button, and the following dialog will be displayed.
This dialog presents the complete dependency tree of the service. To disable any particular dependency, all you need to do is "uncheck" it and press the "OK" button.
Important to note that after configuring your dependencies you have to save the service configuration, in order to have the generated war file reflecting your configuration.
A scorecard is a graphical representation of a formula used to calculate an overall score. A scorecard can be used to predict the likelihood or probability of a certain outcome. Drools now supports additive scorecards. An additive scorecard calculates an overall score by adding all partial scores assigned to individual rule conditions.
Additionally, Drools Scorecards will allows for reason codes to be set, which help in identifying the specific rules (buckets) that have contributed to the overall score. Drools Scorecards will be based on the PMML 4.1 Standard.
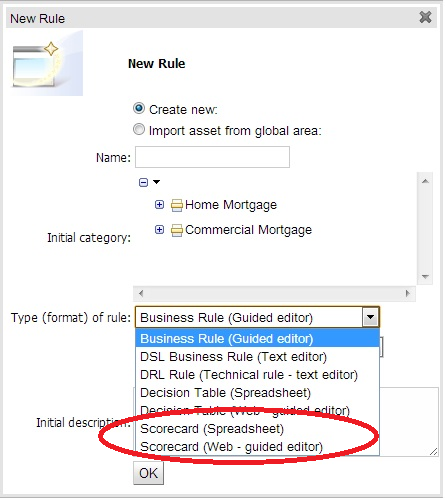
The New Rule Wizard now allows for creation of scorecard assets.
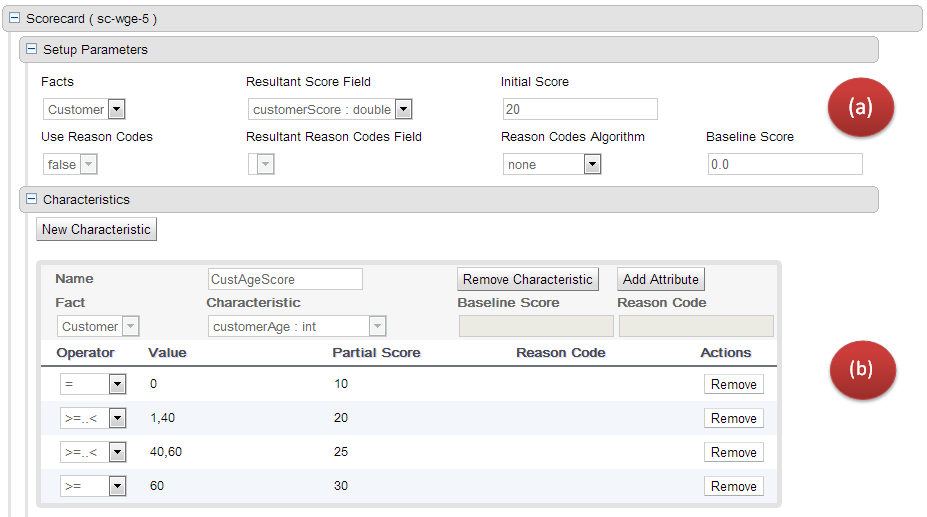
The above image shows a scorecard with one characteristic. Each scorecard consists of two sections (a) Setup Parameters (b) Characteristic Section
The setup section consits of parameters that define the overall behaviour of this scorecard.
Facts: This dropdown shows a list of facts that are visible in this package. These are classes that are imported into this package.
Resultant Score Field: Shows a list of fields from the selected fact. Only fields of type 'double' are shown. If this dropdown is empty double check your fact model. The final calculated score will be stored in this field.
Initial Score: Numeric Text Field to capture the initial score. The generated rules will initialize the 'Resultant Score Field' with this score and then is added to the overall score whenever partial scores are summed up.
Use Reason Codes: Boolean indicator to compute reason codes along with the final score. Selecting Yes/No in this field will enable/disable the 'Resultant Reason Codes Field', 'Reason Code Algorithm' and the 'Baseline Score' field.
Resultant Reason Codes Field: Shows a list of fields from the selected fact. Only fields of type 'java.util.List' are shown. This collection will hold the reason codes selected by this scorecard.
Reason Code Algorithm: May be "none", "pointsAbove" or "pointsBelow", describing how reason codes shall be ranked, relative to the baseline score of each Characteristic, or as set at the top-level scorecard.
Baseline Score: A single value to use as the baseline comparison score for all characteristics, when determining reason code ranking. Alternatively, unique baseline scores may be set for each individual Characteristic as shown below. This value is required only when UseReasonCodes is "true" and baselineScore is not given for each Characteristic.
Note
If UseReasonCodes is "true", then BaselineScore must be defined at the Scorecard level or for each Characteristic, and ReasonCode must be provided for each Characteristic or for each of its input Attributes. If UseReasonCodes is "false", then baselineScore and reasonCode are not required.
On Clicking the 'New Characteristic' button, a new empty characteristic editor is added to the scorecard. Defines the point allocation strategy for each scorecard characteristic (numeric or categorical). Each scorecard characteristic is assigned a single partial score which is used to compute the overall score. The overall score is simply the sum of all partial scores. Partial scores are assumed to be continuous values of type "double".
Name: Descriptive name for this characteristic. For informational reasons only.
Remove Charteristic: Will remove this characteristic from the scorecard after a confirmation dialog is shown.
Add Attribute: Will add a line entry for an attribute (bin).
Fact: Select the class which will be evaluated for calculating the partial score.
Characteristic: Shows the list of fields from the selected Fact. Only fields of type "String", "int", "double", "boolean" are shown.
Baseline Score: Sets the characteristic's baseline score against which to compare the actual partial score when determining the ranking of reason codes. This value is required when useReasonCodes attribute is "true" and baselineScore is not defined in element Scorecard. Whenever baselineScore is defined for a Characteristic, it takes precedence over the baselineScore value defined in element Scorecard.
Reason Code: Contains the characteristic's reason code, usually associated with an adverse decision.
On Clicking the 'New Attribute' button, a new empty attribute editor. In scorecard models, all the elements defining the Attributes for a particular Characteristic must all reference a single field.
Operator: The condition upon which the mapping between input attribute and partial score takes place. The operator dropdown will show different values depending on the datatype of the selected Field.
DataType Strings: "=", "in".
DataType Integers: "=", ">", "<", ">=", "<=", ">..<", ">=..<", ">=..<=", ">..<=".
DataType Boolean: "true", "false".
Refer to the next sub-section (values) for more details.
Value: Basis the operator selected the value specified can either be a single value or a set of values separated by comma (","). The value field is disabled for operator type boolean.
Table 4.1. Operators / Values Data Type Operator Value Remarks String = Single Value will look for an exact match String in Comma Separated Values (a,b,c,...) The operator 'in' indicates an evaluation to TRUE if the field value is contained in the comma separated list of values Boolean is true N/A Value Field is uneditable (readonly) Boolean is false N/A Value Field is uneditable (readonly) Numeric = Single Value Equals Operator Numeric > Single Value Greator Than Operator Numeric < Single Value Less Than Operator Numeric >= Single Value Greater than or equal To Numeric <= Single Value Less than or equal To Numeric >..< Comma Separated Values (a,b) (Greater than Value 'a') and (less than value 'b') Numeric >=..< Comma Separated Values (a,b) (Greater than or equal to Value 'a') and (less than value 'b') Numeric >=..<= Comma Separated Values (a,b) (Greater than or equal to Value 'a') and (less than or equal to value 'b') Numeric >..<= Comma Separated Values (a,b) (Greater than Value 'a') and (less than or equal to value 'b') Partial Score: Defines the score points awarded to the Attribute.
Reason Code: Defines the attribute's reason code. If the reasonCode attribute is used in this level, it takes precedence over the ReasonCode associated with the Characteristic element.
Actions: Delete this attribute. Prompts the user for confirmation.
Note
If Use Reason Codes is "true", then Baseline Score must be defined at the Scorecard level or for each Characteristic, and Reason Code must be provided for each Characteristic or for each of its input Attributes. If Use Reason Codes is "false", then BaselineScore and ReasonCode are not required.